Fig. 5. Transgenic rescue of slp expression and function by subsets of CRMs.
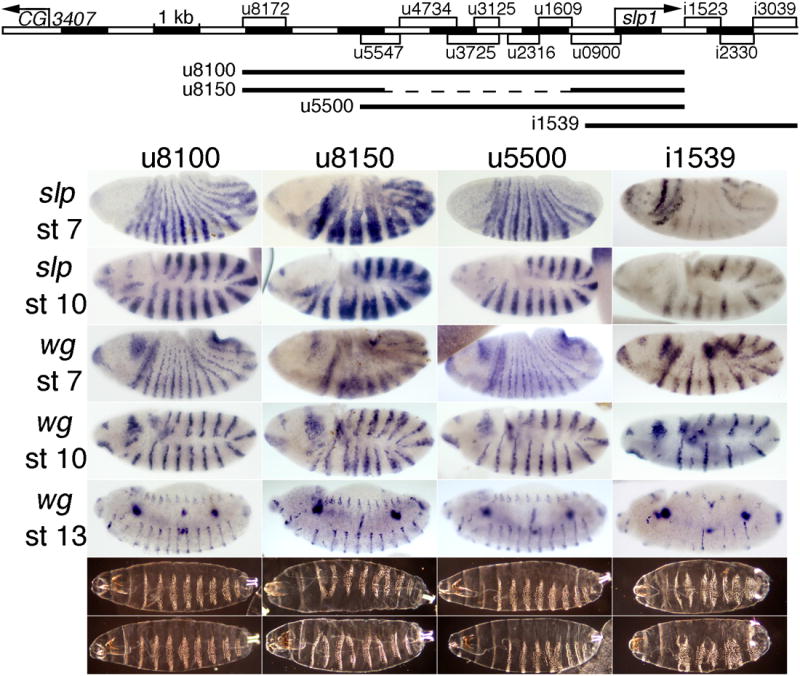
The map at the top indicates the extent of each rescue construct as a line below the map of all the stripe CRMs of the slp locus. The panels below show embryonic expression of slp RNA at stages 7 (top row) and 9-10 (2nd row), wg expression at stages 7, 10, and 13-14 (indicated on the left), and cuticles at the end of embryogenesis (bottom rows show the range of patterns seen) in a slp RNA null mutant (slpΔ34) with a transgene carrying the slp locus from: 1st column: –8076 to +1539 bp relative to the slp1 TSS, which includes 78 bp 3′ of the slp1 mRNA polyA signal. Note the near-complete rescue (see Fig. 4 for wild type). 2nd column: -8076 to -5000, fused with –940 to +1539 bp. Note the ectopic expression of both slp and wg at stages 7 and 10, and the partial loss of wg and naked cuticle at later stages. 3rd column: –5510 to +1539 bp. Note the near-complete rescue, with more severe defects in the denticle pattern in some embryos, relative to column 1. 4th column: –665 to +3934 bp. Note the loss of expression of both slp and wg, more severely in alternate parasegments, at all stages (see text), and the pair-rule loss of naked cuticle. All constructs were analyzed at the same chromosomal location (see Material and Methods).
