Fig. 6.
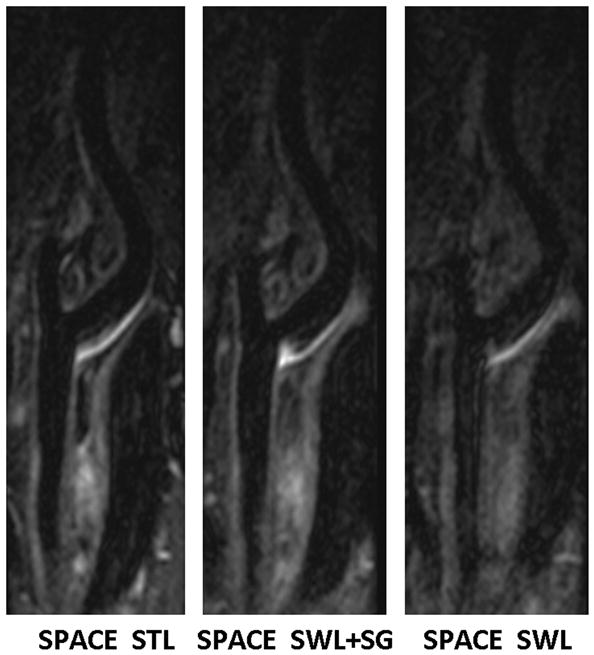
Comparison of location-matched longitudinal MPR images obtained from the “SPACE STL”, “SPACE SWL+SG”, and “SPACE SWL” scans, respectively, in a 45-year-old male volunteer. Shown are three 2-mm-thick images reconstructed from the 3D image sets. Swallowing was shown to induce severe overall image degradation, obscure wall boundary, and reduce the wall-to-background contrast. The proposed SG approach makes SPACE immune to swallowing motion, providing good artery wall delineation and high wall-to-background contrast that is comparable to “SPACE STL” imaging. All images are displayed with the same window level.
