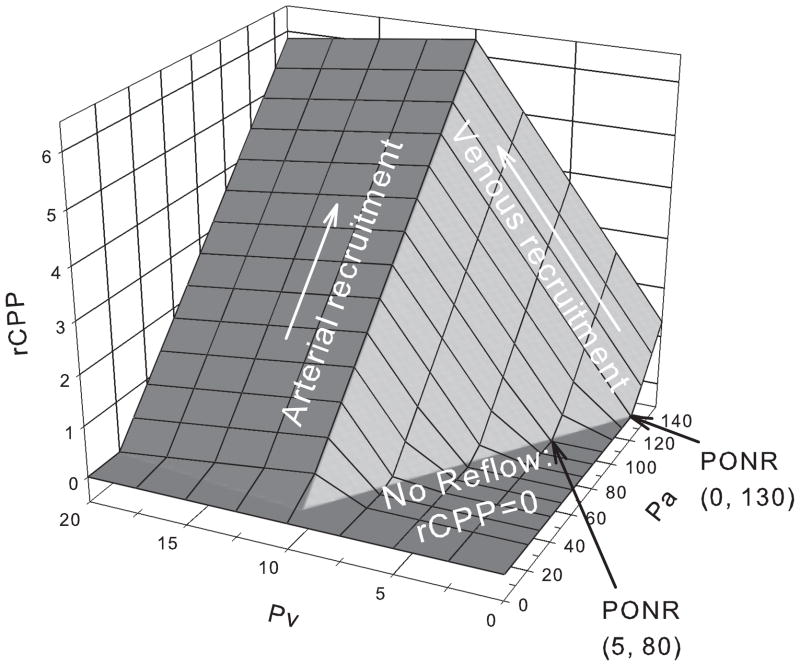
Fig. 4. Arterial and venous augmentation of core perfusion pressure.
(Pcore =10; Ppen=0). Pa is increased from 0 to 150mmHg, while Pv from 0 to 20. Regional cerebral perfusion pressure decreases to zero when Pv<=5 and Pa<=80. If venous pressure is zero, Pa has to exceed 130mmHg to increase rCPP above zero. Note the scale difference for the arterial and venous pressures.