Fig. 1. Tuning shifts, the auditory pathway and auditory cortex.
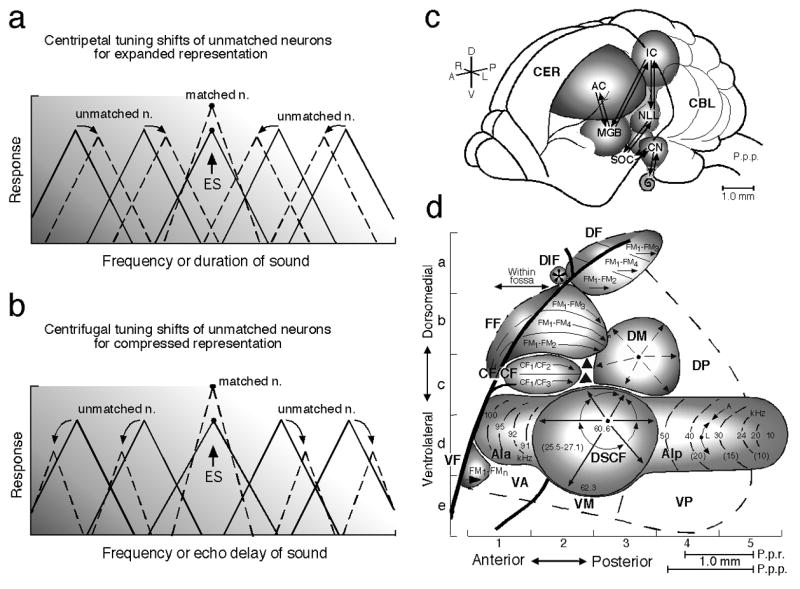
Focal electric stimulation (ES) of the lemniscal auditory system evokes facilitation, inhibition and tuning shifts in AI and subcortical auditory nuclei. There are two types of tuning shifts of “tuning-unmatched” neurons: centripetal (a) and centrifugal (b). (a) and (b) The unbroken and broken triangles represent the tuning curves in the control and shifted conditions, respectively. “Tuning-matched” neurons do not show tuning shifts, but facilitation of their auditory responses. Centripetal and centrifugal tuning shifts both have been found in the frequency and time domains. (c) The dorsolateral view of the brain of the mustached bat, Pteronotus parnellii parnellii (P.p.p.). The arrows indicate the ascending and descending (corticofugal) systems. (d) A neurophysiological map of the auditory cortex (AC) of the mustached bat. The numbers and lines in the anterior (AIa) and posterior (AIp) divisions and the Doppler-shifted constant frequency (DSCF) area in AI indicate iso-best-frequency lines. The CF/CF area sensitive to combinations of constant-frequency (CF) signals consists of two subdivisions that contain a Doppler-shift (velocity) axis. The frequency modulation-frequency modulation (*FF), dorsal fringe (DF) and ventral fringe (VF) areas are sensitive to combinations of frequency-modulated (FM) signals. Each area consists of three subdivisions. These areas contain an echo-delay (range) axis. CBL, cerebellum; CER, cerebrum; CN, cochlear nucleus; DIF, dorsal intrafossa area; DM, dorsomedial area; DP, dorsoposterior area; IC, inferior colliculus; MGB, medial geniculate body; NLL, nucleus of the lateral lemniscus; P.p.r., Pteronotus parnellii rubiginosus which is larger than P.p.p.; SOC, superior olivary complex; VA, ventroanterior area; VM, ventromedial area; VP, ventroposterior area (Suga and Ma 2003). Focal electric stimulation of the AIp, DF or VF area evokes centripetal tuning shifts, whereas that of the DSCF or FF area evokes centrifugal tuning shifts. [*The FF area had been called the FM-FM area because it consists of FM-FM combination-sensitive neurons. Both the DF and VF areas, subsequently found, also consist of FM-FM neurons. So, the FM-FM area is now called the FF area (Tang and Suga 2008).]
