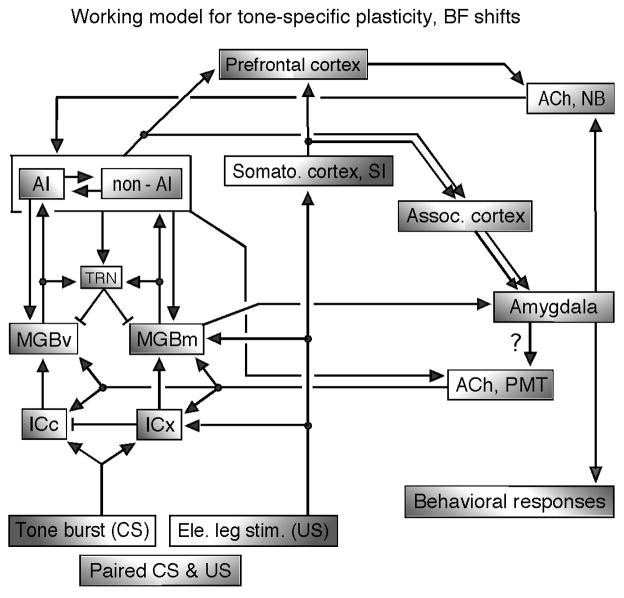
Fig. 11. A working model for tone-specific plasticity (BF shifts) elicited by auditory fear conditioning, paired CS – US.
ACh, acetylcholine; AI, primary auditory cortex; CS, conditioned stimulus (tone bursts); ICc and ICx, central nucleus and external cortex of the inferior colliculus; MGBv and MGBm, ventral and medial divisions of the medial geniculate body; NB, nucleus basalis in the forebrain; non-AI, auditory cortex other than AI; PMT, pontomesencephalic tegmentum; TRN, thalamic reticular nucleus; US, unconditioned stimulus (electric leg-shock). The short bar at the end of a line means a projection from inhibitory neurons. The conditioning elicits the cortical BF shift through the neural net in AI, corticofugal feedback loop and ACh from the NB, and also the collicular BF shift through the corticofugal feedback and ACh from the PMT. See the text (revised version of Suga et al. 2000).