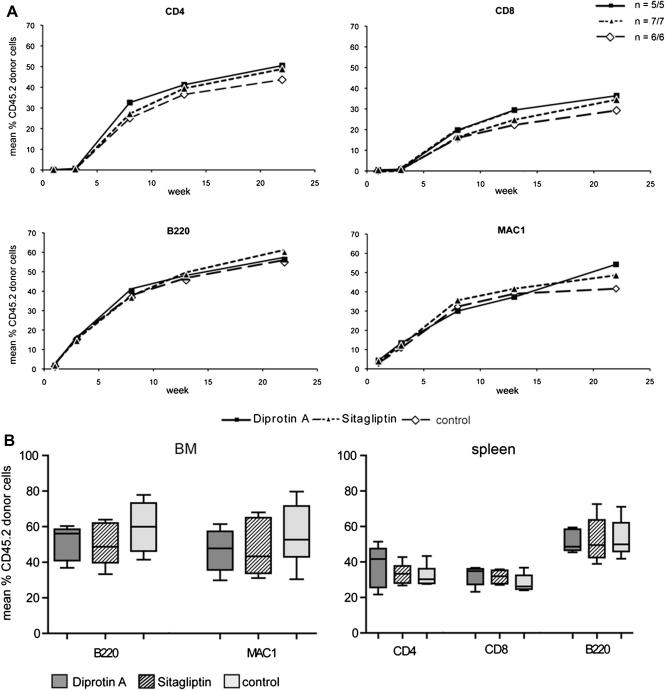
Figure 2.
Chimerism after transplantation of congenic BMCs after combined treatment with Diprotin A in vitro and in vivo and after in vivo treatment with sitagliptin. Recipient mice were conditioned with 1 Gy TBI and received 10 × 106 congenic CD45.2 BMCs (n = 6/control group C, n = 5/Diprotin A–treated group D, n = 7/sitagliptin-treated group E). In group D, BMC were treated in vitro with 5 mM Diprotin A before transplantation and, in addition, recipients were treated in vivo with Diprotin A (4 μmol IV day 0 and 5 μmol Diprotin A subcutaneously every 12 hours for 3 days). Recipients of group E were treated with sitagliptin orally. Levels of chimerism in blood over time (A) were determined by flow cytometry and are presented as means for Diprotin A–treated (squares), sitagliptin-treated (dotted line with triangle) and untreated (dotted line with diamonds) groups. In (B) chimerism in BM and spleen at the end of follow-up is depicted in box and whisker plots. No significant differences were noted between both groups.