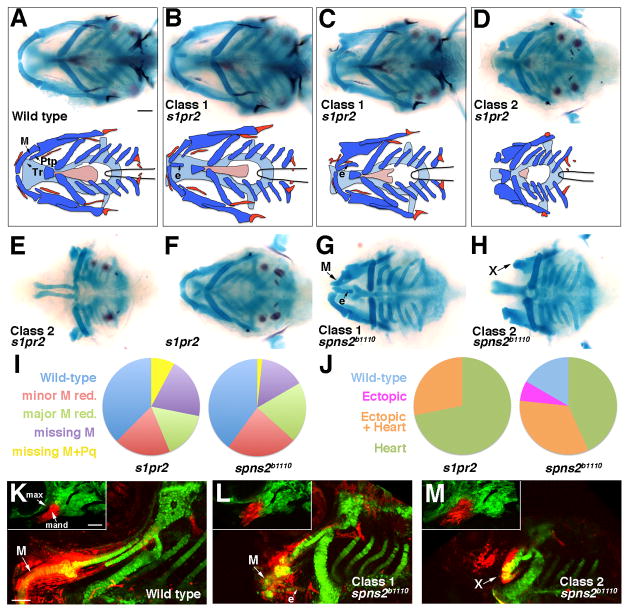
Figure 1. Jaw skeletal defects in s1pr2 and spns2b1110 mutants.
(A–H) Ventral views show head skeletons of 6 dpf zebrafish larvae stained for cartilage (blue) and bone (red) in (A–F) and cartilage only in (G, H). Bottom schematics in (A–D) show facial cartilage (dark blue), neurocranial cartilage (light blue), and bone and teeth (red). Meckel’s (M), pterygoid process (Ptp), and trabecular (Tr) cartilages are indicated. s1pr2 and spns2b1110 larvae variably displayed ectopic (e) midline cartilage (Class 1: B, C, G) and/or graded reductions of jaw and anterior neurocranial skeleton (Class 2: D, E, H). In addition, some genotypically mutant s1pr2 and spns2b1110 larvae displayed a normally patterned jaw (F).
(I and J) Pie charts show proportions of s1pr2 (n = 32) and spns2b1110 (n = 30) larvae showing progressive reductions of jaw skeleton (I, scored for each side) and ectopic cartilage and/or heart defects (J, scored for each animal). Minor M reduction refers to losses of less than 50% of the cartilage (e.g. C, G) and major M reduction losses greater than 50% (e.g. top of D). More severe categories include missing M (e.g. bottom D) and missing M + Pq (e.g. E). Wild-type siblings never displayed defects.
(K–M) sox10:kikGR imaging of the mandibular and hyoid arches at 30 hpf (insets) and the resulting skeletal derivatives at 5 dpf. Photoconversion of mandibular (mand) prominence CNCCs (red) resulted in labeling of Meckel’s (M) cartilage and surrounding mesenchyme in wild types (n = 3/3). In spns2b1110; sox10:kikGR larvae, mandibular CNCCs generated either malformed M and ectopic (e) midline cartilages (L, n = 3/9) or very reduced remnants (“X”) (M, n = 6/9). Max, maxillary prominence. Scale bars = 50 μm.