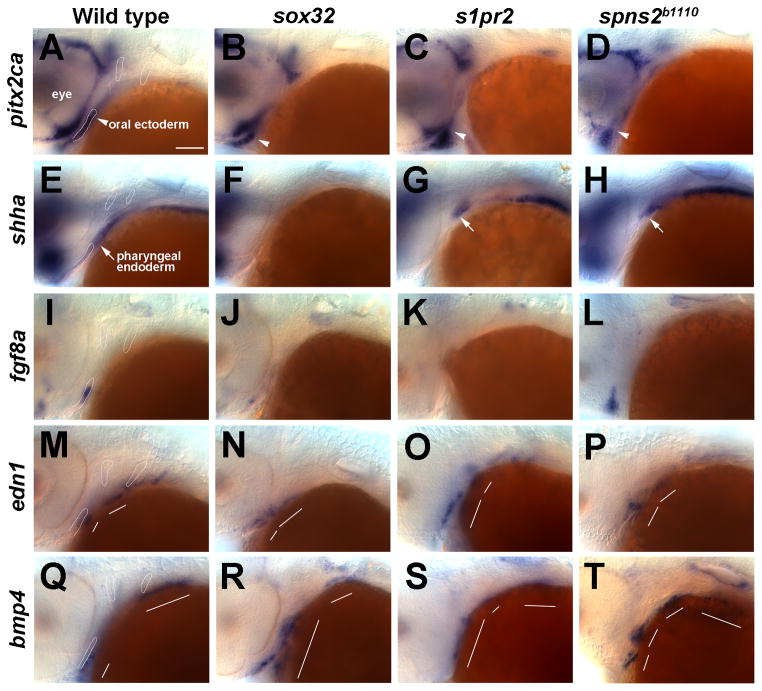
Figure 3. Facial ectoderm gene expression in endoderm mutants.
(A–T) In situ hybridizations at 36 hpf. In wild types, pitx2ca (A), shha (E), and fgf8a (I) are expressed in oral ectoderm and edn1 (M) and bmp4 (Q) in aboral ectoderm. pitx2ca expression in the oral ectoderm (arrowheads) is present but shifted anteriorly in sox32 (B, n = 6/6), s1pr2 (C, n = 11/11), and spns2b1110 (D, n = 4/4) embryos. The expression of shha in the oral ectoderm is lost in all mutants, whereas endoderm expression (arrows) is absent in sox32 mutants (F, n = 7/7), variably posteriorly displaced (G, n = 10/15) or disorganized (see Fig. 4, n = 3/15) in s1pr2 mutants, and variably posteriorly displaced (H, n = 6/7) or disorganized (not shown, n = 1/7) in spns2b1110 mutants. fgf8a expression is reduced in sox32 mutants (J, n = 6/6), reduced (K, n= 4/10) or disorganized (not shown, n= 4/10) in s1pr2 mutants, and reduced (not shown, n= 13/27) or disorganized (L, n= 14/27) in spns2b1110 mutants. edn1 expression in the first two arches (white lines) is present but disorganized in sox32 (N, n = 8/8), s1pr2 (O, n = 6/6), and spns2b1110 (P, n = 5/5) mutants. bmp4 expression is also disorganized in sox32 (R, n = 6/6), s1pr2 (S, n = 7/7), and spns2b1110 (T, n = 5/5) mutants. Outlines of the oral ectoderm and first two pouches are shown for wild types. Scale bar = 50 μm.