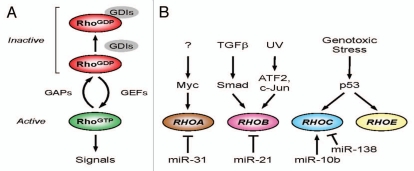
Figure 1.
Regulating Rho GTPase activity and expression. (A) Rho GTPases act as molecular switches to regulate downstream signal transduction pathways. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) promote GTP exchange, converting the GDP-bound form (RhoGDP) to the GTP-bound active form (RhoGTP). GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) promote GTP hydrolysis and return the GTPase to its inactive form. (B) Transcriptional regulation of Rho family GTPases. RHOA gene expression can be positively and negatively regulated by Myc and miR-31, respectively. TGFβ signaling via the Smad3,4 transcription factor complex leads to increased transcription of RHOB. RHOB mRNA expression is also upregulated by the ATF2 and c-Jun transcription factors in response to UV irradiation. Stabilization and activation of p53 by genotoxic stresses promotes the transcription of RhOC and RHOE. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) can also regulate Rho family gene expression by a variety of post-transcriptional mechanisms.