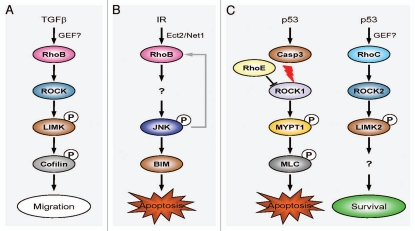
Figure 2.
Context-dependent regulation of Rho GTPase signaling. (A) TGFβ-dependent regulation of RhoB activity. TGFβ upregulates RhoB expression by a MEK/ERK-dependent and Smad-dependent pathway. Once activated, RhoB signals through the ROCK-LIMK pathway to alter cell motility and migration. (B) RhoB-dependent cell death following DNA damage. Ionizing radiation (IR) triggers the DNA damage response to activate Ect2 and Net1. These GEFs promote the GTP exchange and activation of RhoB. Activated RhoB signals via the JNK pathway to induce the pro-apoptotic protein BIM and cell death. A positive feedback loop might allow JNK phosphorylation to further increase RHOB transcription and amplify RhoB-dependent cell death. (C) p53 regulates pro-survival functions of Rho GTPases. Caspase-3 is activated in response to genotoxic stress and cleaves and activates ROCK1. This kinase phosphorylates a number of substrates (including MYPT1 and MLC), which modify the actin cytoskeleton and ultimately generate contractile force within the cell. This increased contractility provides the force required for apoptotic membrane blebbing and disruption of the nucleus. RhoE can bind and inhibit ROCK1 activity, thereby promoting cell survival. A separate pro-survival pathway is triggered downstream of p53 by the upregulation and activation of RhoC and LIMK2. Signaling via an as yet unknown substrate of LIMK2 promotes cell survival.