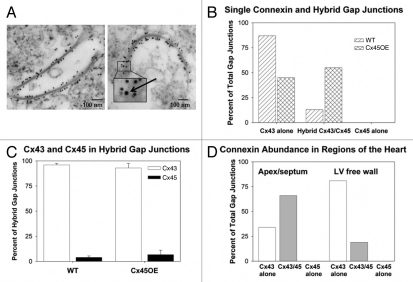
Figure 2.
Immunogold electron microscopy of cardiac connexins in hybrid (heteromeric and/or heterotypic) gap junctions. (A) Electron micrographic images of gap junctions decorated with 10 nm gold particles conjugated with anti-Cx43 antiserum (left), and a gap junction containing a 20 nm gold particle conjugated to anti-Cx45 antiserum (inset, arrow) among numerous 10 nm gold particles conjugated to anti-Cx43 antibody (right). Bar = 100 nm. (B) Proportions of Cx43-bound gold particles and Cx45-bound gold particles as a percent of total gap junctions in gap junction-enriched membrane preparations isolated from wild-type (WT) and Cx45OE hearts. WT hearts exhibited a larger percentage (87%) of homomeric/homotypic Cx43 gap junctions. In contrast, the percentages of Cx43 only and heteromeric gap junctions in Cx45OE hearts were roughly equivalent. Cx45 homomeric/homotypic gap junctions were not found in either WT or Cx45OE hearts. (C) The percentage of Cx43 and Cx45 in heteromeric gap junction channels was comparable in WT and Cx45OE hearts, despite the fact that there was a greater proportion of heteromeric gap junction channels in Cx45OE hearts. (D) Relative proportions of Cx43 homomeric/homotypic and Cx43/Cx45 heteromeric gap junctions by gross regions of the hearts. More heteromeric gap junctions were observed in the apex/septum compared to the LV free wall consistent with known expression of Cx45 in the cardiac conduction system which is concentrated in the subendocardial interventricular septum and in the distal Purkinje system.