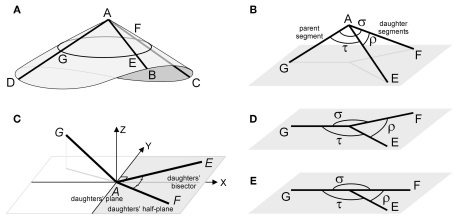
Figure 1.
(A) A schematic 3D bifurcation with DA a parent segment and AB and AC the daughter segments. The points G, E, and F on these segments are at unit distance from A. A right circular cone is wrapped around the bifurcation DABC with a circular cross section through G, E, and F. (B) A spatial bifurcation with unit lengths segments, the intermediate angle ρ between the daughter segments, and the side angles σ and τ, between the parent and each of the daughter segments, respectively. (C) An aligned bifurcation with the daughter segments defining the daughter plane (X–Y plane) and the daughters’ bisector coinciding with the positive X-axis. The daughter half-plane contains the daughter segments and is bounded by the Y-axis. (D–E) Two examples of flat bifurcations.