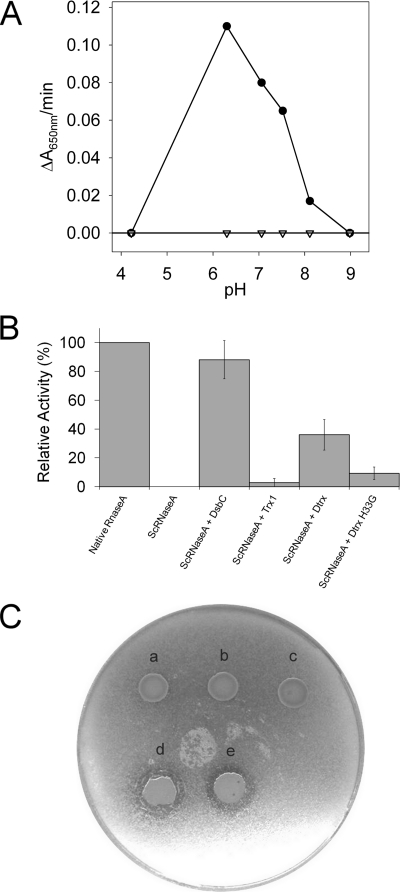
FIGURE 1.
Dtrx activities. A, insulin reduction assay by Trx1 and Dtrx as a function of pH. The disulfide reductase activity was determined by using the insulin reduction assay. The assay was performed at 306 K with 2 μm Dtrx (triangle) or 2 μm Trx1 (black circle). The catalyzed reduction of insulin (100 μm) was followed by measuring an increase in absorbance at 650 nm and evaluated at different pH levels: 4.22, 6.3, 7.06, 7.52, 8.11, and 8.98. The absorbance caused by the nonenzymatic insulin reduction by DTT (1 mm) is substracted. B, scrambled RNase A (ScRNase) refolding assay: yield of RNase A activity of native RNase A and reshuffling of ScRNase A after incubation with DsbC, Trx1, Dtrx, and Dtrx H33G mutant. For the determination of a percentage of the RNase A activity, the mean intensity of several isolated peaks in RNA spectrum was used relative to the RNA spectrum in the presence of native RNase A. The RNA spectrum in presence of ScRNase A is used as blank. The error analysis of the data points was performed using Excel software. C, study of in vivo activity. Qualitative visualization of PalB activity using tributyrin plate for recombinant E. coli TG1 and Rosetta-gami as host cells. Different expression systems were observed: pJF119EH PalB (a), pJF119EH Dtrx-PalB (b), pJF119EH Trx1-PalB (c) in E. coli TG1 and pJF119EH PalB (d) and pJF119EH Dtrx-PalB (e) in E. coli Rosetta-gami.