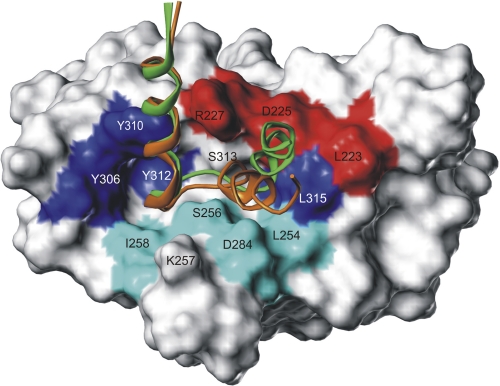
FIGURE 7.
Superimposed interaction models of ECL2 for Cld3 and Cld4 bound to the surface of the cCPE structure. cCPE residues identified by mutation as binding sensitive preferentially for Cld3 (cyan) or for Cld4 (red) are discrete located at the lower and upper rim of the binding pocket. The ECL2 helix-turn-helix models demonstrate common (N-terminal helix) but also partly differing binding modes (C-terminal helix) between Cld3 (orange) and Cld4 (green). This opposing helix tilt is caused by the variant helix capping sequence motifs 152PEA154 and 153ASG155, of Cld3 and Cld4, respectively (side chains not visualized for clarity, see Fig. 4D) Thus, the C-terminal ECL2 helix of Cld3 is tilted toward residues showing stronger mutational effects on Cld3 binding (cyan), whereas that of Cld4 is tilted to residues exhibiting stronger effects on Cld4 binding (red). Residues previously shown to participate in Cld4 binding are labeled in blue.