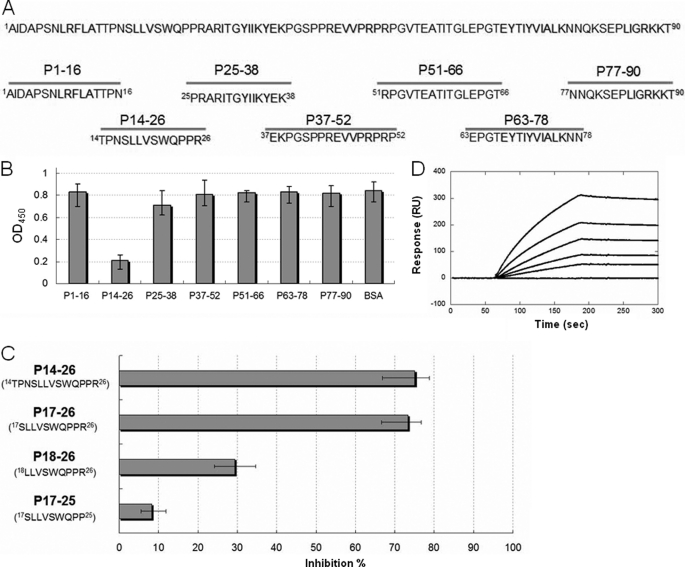
FIGURE 4.
Peptide inhibition assay using synthetic peptides. A, schematic diagram showing the seven peptides (lower panel) synthesized based on the sequence of Fn14 (upper panel). B, peptide inhibition assay measured by ELISA. Peptide 14–26 (P14–26) possessed the highest inhibition potency among all peptides. BSA served as a negative control. C, optimal peptide length determination. Peptide deletion of P14–26 with three residues at the N terminus (P17–26) harbored near-full inhibition activity. Peptide derivatives of P17–26 with one residue deleted at the N terminus (P18–26) and the C terminus (P17–25) showed the reduced inhibition abilities of 61 and 89%, respectively (compared with P14–26). D, KD determination of P17–28 to MAP Ag85B by SPR analysis. The measured kon, koff, and KD values were 33.8 ± 2.6 m−1 s−1, 1.4 ± 0.5 × 10−5 s−1, and 414.2 ± 13.6 nm, respectively. Values represent the mean ± S.E.