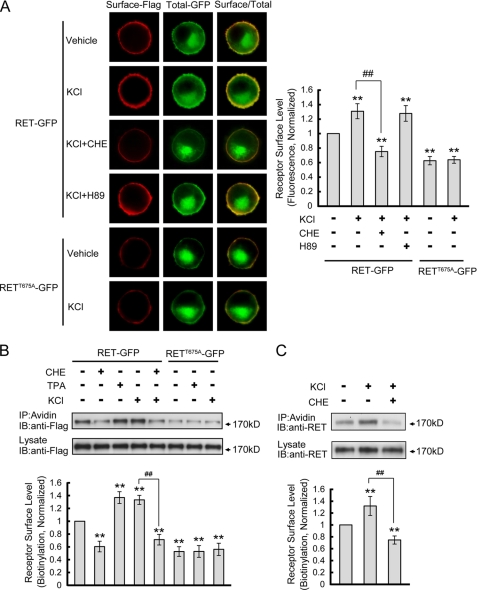
FIGURE 8.
Depolarization enhances RET cell surface levels through PKC but not PKA activation. A, PC12 cells transfected with RET-GFP or RETT675A-GFP were treated with 50 mm KCl for 30 min in the presence of various inhibitors. Receptor surface levels were determined using ratiometric fluorescence assay and normalized to that of RET-GFP in vehicle-treated cells. The results are represented as mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments (**, p < 0.01 versus RET surface levels in vehicle-treated group; ##, p < 0.01 versus RET surface levels in KCl-treated group; one-way ANOVA). B, receptor surface levels under various conditions were quantified by biotinylation methods in transfected PC12 cells. Relative receptor surface levels were normalized to that of RET-GFP in vehicle-treated cells. The results are represented as mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments (**, p < 0.01 versus RET surface levels in vehicle-treated group; ##, p < 0.01 versus RET surface levels in KCl-treated group; one-way ANOVA). C, effect of depolarization on endogenous RET surface expression was determined in cultured DRG neurons. RET cell surface levels were quantified by surface biotinylation in DRG neurons after KCl treatment with or without CHE pre-incubation. Relative RET surface levels were normalized to that of vehicle-treated neurons. The results are represented as mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments (**, p < 0.01 versus RET surface levels in vehicle-treated group; ##, p < 0.01 versus RET surface levels in KCl-treated group; one-way ANOVA).