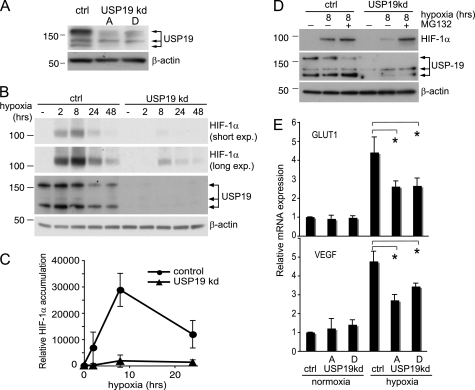
FIGURE 5.
Loss of USP19 impairs hypoxic response. A, Western blot experiment assessing the efficiency of two different shRNA-expressing vectors, pRETRO-SUPER-USP19A (indicated by A) and pRETRO-SUPER-USP19D (indicated by D), in suppressing USP19 protein expression. ctrl, control; kd, knockdown. B, 3 days after transfection, HeLa cells transfected with the empty control plasmid pRETRO-SUPER or pRETRO-SUPER-USP19A were exposed to hypoxia or kept in normoxia as indicated. Western blots were probed anti-HIF-1α (short and long exposure (exp.)) to investigate the effect by USP19 knockdown on HIF-1α accumulation. β-Actin was included as control. C, quantification by densitometry from short exposure Western blots of three independent experiments performed as in Fig. 4B. Values represent relative induction of HIF-1α during hypoxia as compared with normoxia, mean ± S.D. D, same experimental setup as in Fig. 4B, but cells exposed to hypoxia for 8 h were treated in parallel with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10 μm). The results illustrate a continuous proteasomal degradation of HIF-1α during hypoxia in cells with suppressed USP19 expression, E, knockdown of USP19 impairs the HIF-1α transcriptional response during hypoxia. Relative mRNA expression was assessed by qPCR of the HIF-1α target genes GLUT1 and VEGF in cells with or without USP19 knockdown ± hypoxia. Values represent expression levels relative to β-actin mRNA ± S.D. from four independent experiments. *, p values < 0.05 for indicated comparisons.