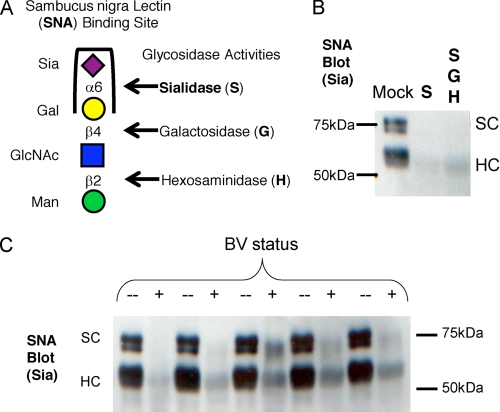
FIGURE 2.
Removal of α2–6-linked sialic acid on secretory component and heavy chain of SIgA by BV vaginal specimens but not normal controls. Vaginal samples from BV-positive women with high levels of sialidase activity, alongside matched healthy controls, were used to process SIgA in overnight incubations in 50 mm sodium acetate buffer at 37 °C. A, the treatment of human colostrum SIgA with sialidase from A. ureafaciens results in a loss of SNA lectin binding, indicating removal of α2–6-linked sialic acids. B, control treatment of SIgA with purified AUS abolishes SNA reactivity. C, SNA reactivity was lost in treatments of SIgA with BV samples but maintained with normal controls.