FIGURE 7.
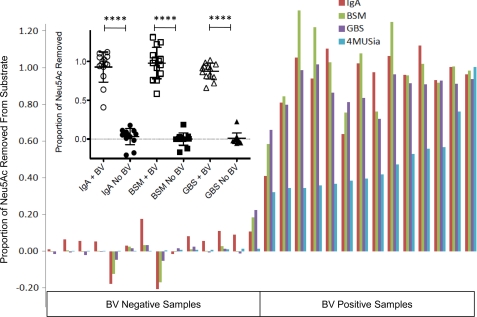
BV sialidases act on sialic acids presented in multiple contexts relevant to the reproductive mucosa. BV specimens containing high levels of sialidase were incubated alongside matched controls (n = 14 each) with macromolecules bearing terminal sialic acids in different contexts. Released sialic acid was quantified by derivatization and HPLC as described in “Experimental Procedures” to assess the ability of BV sialidases to cleave different types of sialic acid-containing substrates. All of the data were normalized to total sialic acid (Neu5Ac) released by digestion with A. ureafaciens sialidase, shown in separate experiments to result in complete release as compared with acid hydrolysis. All of the substrates tested, including 2,3-linked sialic acids from the group B Streptococcus (GBS) capsule and primarily O-linked sialo-glycans from bovine submaxillary mucin (BSM), were desialylated to near completion by BV samples, whereas control specimens had little evidence of sialic acid hydrolysis. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to examine statistical significance (p < 0.0001 for all substrates; inset). The levels of sialidase activity (4MUSia) indicated for each sample are initial rates normalized relative to the sample with highest activity level.