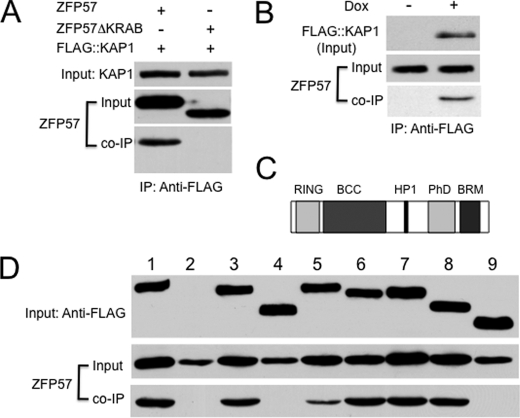
FIGURE 1.
ZFP57 binds to the BCC domain of KAP1 via its KRAB box. FLAG-tagged KAP1 or KAP1 deletion mutants were co-expressed in COS cells with ZFP57 or the ZFP57 deletion mutant without the KRAB box (ZFP57ΔKRAB). The monoclonal antibody against the FLAG epitope was used to precipitate KAP1-associated proteins, and the polyclonal antibodies against ZFP57 were used to probe the immunoprecipitate. A, PCR was used to create the cDNA for ZFP57ΔKRAB. FLAG-tagged KAP1 was co-expressed with ZFP57 or ZFP57ΔKRAB in COS cells. B, doxycycline-inducible ES clones that can express FLAG-tagged KAP1 were isolated from A2lox ES cells (47). Co-IP was performed for ES cells grown in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 1 μg/ml of doxycycline (Dox). C, a diagram for the functional domains of KAP1. HP1, HP1-binding motif. The RING and BCC domains together form the RBCC domain. D, PCR was used to generate the cDNAs encoding KAP1 deletion mutants that lack one or two functional domains of KAP1. Lane 1, wild-type KAP1; lane 2, vector only (pcDNA3-FLAG); lane 3, KAP1ΔRING; lane 4, KAP1ΔBCC; lane 5, KAP1ΔHP1; lane 6, KAP1ΔPhD; lane 7, KAP1ΔBRM; lane 8, KAP1ΔPhD-BRM (lacking both PhD and BRM domains); lane 9, KAP1ΔRBCC.