FIGURE 8.
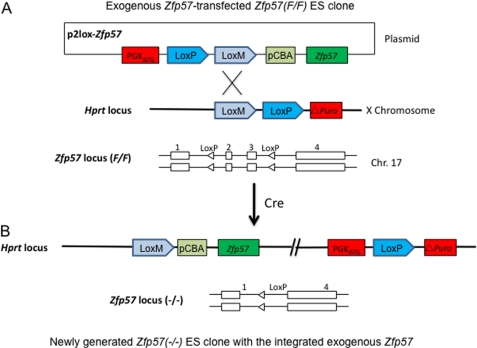
A diagram is shown for the strategy for creating an ES cell system to test the maintenance function of exogenous ZFP57 and its variants. Mouse Zfp57 gene has four exons (exons 1, 2, 3, and 4) and is located on mouse chromosome 17 (26). ES clones containing two floxed alleles of Zfp57 (F/F) were generated by Flp recombinase-mediated excision of the Neo and Zeo cassette flanked by two FRT sites from the targeted allele in the ES clone containing one targeted allele and one floxed allele of Zfp57 (F/T) (26). Homologous recombination was used to insert a puromycin cassette into the hprt locus containing a canonical LoxP site and a mutant LoxM site, as well as a puromycin-resistant gene lacking the initiation codon ATG (△Puro). Similar to the strategy described in the previous study (47), Cre recombinase-mediated recombination was used to generate the ES cell clones for testing whether exogenous ZFP57 or its variants could substitute for the endogenous ZFP57. Diagrams were shown for the ES clone transfected with the plasmid containing the exogenous Zfp57 cDNA before (A) and after (B) Cre recombinase-mediated recombination. A, the cDNA for the wild-type Zfp57 or the mutant Zfp57 under the control of chicken β-actin and CMV promoter was cloned into the p2Lox vector. The resultant plasmid was co-transfected with a mammalian expression plasmid pCAGGS-Cre that constitutively expresses Cre recombinase into ES cells containing two floxed alleles of Zfp57 and a puromycin cassette at the hprt locus located on mouse × chromosome. B, upon transient expression of Cre recombinase, both floxed alleles of Zfp57 were excised. Simultaneously, the constitutive PGK promoter with the initiator codon ATG, together with the cDNA for Zfp57 or its mutants under the control of chicken β-actin and CMV promoter was integrated onto the LoxP and LoxM sites of hprt locus. The subsequent recombination between two LoxP sites results in in-frame fusion of the constitutive PGK promoter containing the initiator codon ATG and the puromycin-resistance gene lacking the initiator codon ATG, allowing expression of the full-length puromycin-resistant gene (47). These puromycin-resistant ES clones will also express the exogenous ZFP57 or its variants under the control of the constitutive chicken β-actin and CMV promoter (pCBA).