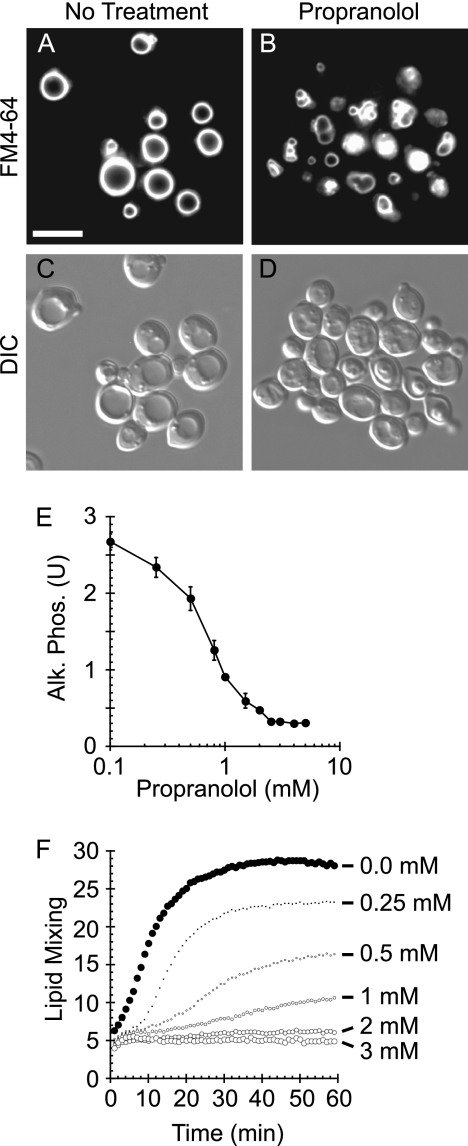
FIGURE 1.
Inhibition of PA phosphatase activity causes vacuole fragmentation and inhibits fusion. Wild type yeast cells were incubated with 5 μm FM4-64 to label vacuoles. Wild type cells were treated with buffer (A and C) or 2 mm propranolol (B and D). Cells were photographed using differential interference contrast (DIC), and FM4-64 images were acquired using a 42 HE CY3 shift-free filter set. Bar, 5 μm. E, vacuoles were harvested from WT BJ3505 (PHO8 pep4Δ) and DKY6281 (pho8Δ PEP4) and tested for fusion by content mixing and proPho8p maturation. Fusion reactions containing 3 μg of each vacuole type were incubated in the absence or presence of the indicated propranolol concentrations. Alk. Phos., alkaline phosphatase. Error bars represent S.E. (n = 3). U, units. F, fusion was examined by a real-time lipid-mixing assay. Donor vacuoles were labeled with Rh-PE at self-quenching concentrations. Labeled donor vacuoles (2 μg) were incubated with 16 μg of unlabeled acceptor vacuoles. Fusion was measured by Rh-PE dequenching. Reactions were treated with buffer or propranolol at the indicated concentrations. The experiment is representative of three trials.