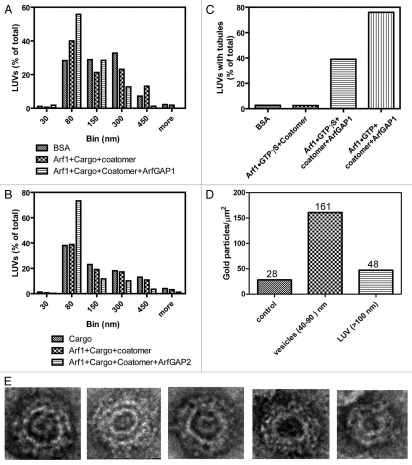
Figure 1.
Effect of ArfGAP1 and ArfGAP2 on LUVs. LUVs were formed by extrusion through membrane with 1.0 µm pore size as described75 and consisted of 40% phosphatidylcholine (PC), 25% phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), 15% phosphatidylserine (PS), 9% phosphatidylinositol (PI), and 10% cholesterol and 1% phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P). LUVs were incubated with the proteins and peptide indicated in the figure at the following concentrations: bovine serum albumin (BSA), 5 µM; myrArf1•GTP⎳S, 0.1 µM; Arf1•GTP, 0.1 µM; ArfGAP1, 0.1 µM; ArfGAP2, 0.1 µM; coatomer, 0.124 µM; palmitoylated p25 peptide, 5 µM. LUVs were imaged by negative stained EM. (A) Effect of ArfGAP1 on LUV size distribution. LUVs were incubated with BSA, p25+Arf1•GTP⎳S+coatomer or p25+Arf1•GTP⎳S+coatomer+ArfGAP1. Diameters of the structures were determined using ImageJ for one of two experiments that were performed. At least 100 LUVs under each condition were examined. (B) Effect of ArfGAP2 on LUV size. The experiment was performed as described in (A) but with the indicated additions. The quantification shown is for one of two experiments. (C) ArfGAP1 induced tubulation of LUVs. The fraction of LUVs containing 2 or more tubules 20 nm in diameter and more than 50 nm in length was determined from the negative stained images. At least 100 LUVs were examined for each condition. (D) Association of coatomer with vesicles. LUVs were immunostained. Coatomer was detected using secondary antibody conjugated to 12 nm gold particles. Gold particles associated with the indicated structures was determined by examination of the negative stained images. The total number of particles associated with each structure is indicated over the bars. (E) Examples of 30–80 nm particles. LUVs were incubated with p25, Arf1•GTP⎳S, Coatomer and ArfGAP2.