Figure 6.
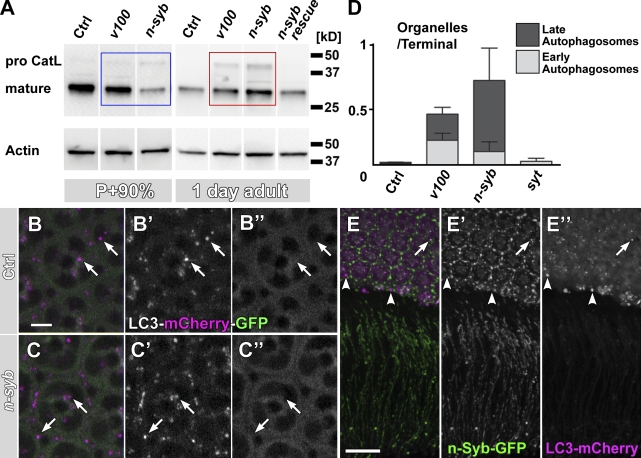
Loss of n-syb causes a primary defect in delivering degradation machinery vesicles to to-be-degraded compartments. (A) Western blot analysis of mutant eyes (n-syb and v100) at P+90% and 1 d after eclosion, probed with an antibody against insect Cathepsin L (CatL). Note that at P+90%, mature Cathepsin is reduced in n-syb compared with control and v100 (blue box) but increased in the adult (red box). (B and C) Live imaging of the Atg8/LC3-mCherry-GFP fusion reporter in wild-type (B) and n-syb (C) photoreceptors. Note that GFP fluorescence, but not mCherry fluorescence, is quenched in an acidification-dependent manner (arrows). (D) Profile counts of early and late autophagosomes based on EM. Examples are shown in Fig. S4. (E) Wild-type cooverexpression of GFP–n-syb and LC3/Atg8-mCherry reveals little colocalization (arrow), large autophagosomes that are n-Syb negative (arrowheads), and no autophagosomes at synapses in wild type. Bars: (B) 5 µm; (E) 10 µm. All error bars are SEM. Ctrl, control.