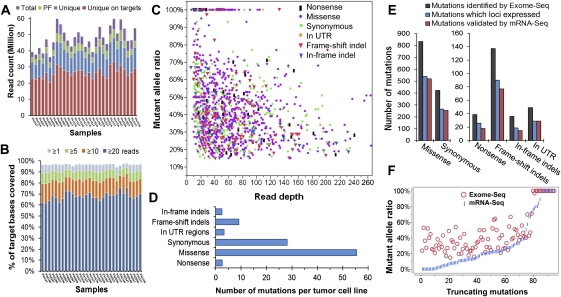
Figure 1.
The performance of Exome-seq and a summary of somatic mutations. (A) The summary of Exome-seq data. For each sample, the number of raw sequence reads (total), passing filter reads (PF), unique reads that mapped in consistent read pairs (unique), and the unique reads that fall within the targeted regions (unique on target) are shown. (B) The sequence coverage of targeted bases. The fraction of the targeted bases that were covered by unique reads at the sequence depth of 1×, 5×, 10×, and 20× is shown. (C) An overview of the somatic mutations identified by Exome-seq. Different markers and colors were used to show different mutation types. (D) The average number of somatic mutations identified per tumor cell line. (E) The performance of mRNA-seq in verification of somatic mutations identified by Exome-seq. The mutations that loci expressed represent those mutations that loci covered by five or more cDNA sequence reads. (F) Validation of the truncating mutations that introduced premature termination codons. The abundance of the mutant alleles in genomic DNA was compared with that of their corresponding cDNA.