Figure 3.
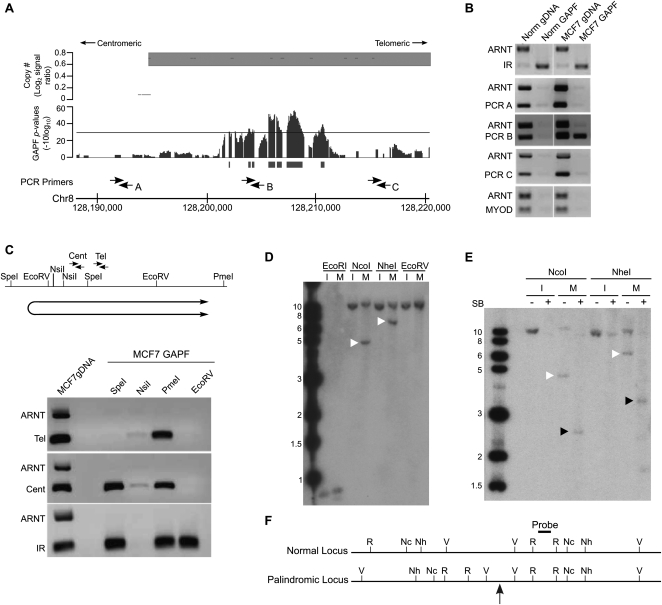
Validation of a de novo DNA palindrome in chromosome 8q24.21 of breast cancer cell line MCF7. (A) GAPF analysis on tiling arrays comparing MCF7 with cultured HFs. The lower graph displays GAPF P-values (−10log10). The solid bars under the graphs represent GAPF-positive regions (P-value [−10log10] > 30, run > 50 bp, gap < 100 bp). The upper graph displays wavelet-derived copy-number segments (average log2 signal ratio). Segments with a log2 signal ratio >0.3 are designated as gained. The locations of PCR primers used in the PCR-enrichment analysis are shown. (B) PCR-based analyses to detect enrichment of genomic loci in 8q24.21 over the nonpalindromic region (ARNT) following GAPF preparations of MCF7 (MCF7 GAPF) and pooled PBL cells (Norm GAPF). Analysis of a normally occurring inverted repeat (IR) and nonpalindromic region (MYOD) are included to confirm efficient GAPF preparations. Note that the only loci that are enriched by GAPF are IR in MCF7 and pooled PBLs, and PCRB in MCF7, located in the GAPF-positive region. (C) PCR-enrichment analysis following targeted restriction-enzyme digestion preceding GAPF. Genomic DNA from MCF7 cells was predigested with SpeI, NsiI, PmeI, or EcoRV, shown on the map, and processed by GAPF. Enrichment of the GAPF-positive region in 8q24.21 over the nonpalindromic ARNT region was examined using two primer pairs, Cent and Tel. Digestion in the nonpalindromic spacer of a palindrome or IR will eliminate enrichment of the sequence by GAPF, as shown by the lack of PCR product when DNA was first digested with NsiI and enrichment of the IR was assessed (bottom gel). Note that enrichment of the 8q24.21 region was seen with the Cent primers when MCF7 DNA was digested with SpeI, but not observed when the Tel primers were used. Based on these analyses, the inferred location and orientation of palindrome places the palindromic center between SpeI and EcoRV restriction sites, shown below the map. (D–F) Southern analysis to detect rearrangements of the GAPF-positive region in 8q24.21. (D) Genomic DNA from MCF7 (M) and normal human fibroblast cell line IMR90 (I) was digested with EcoRI (R), NcoI (Nc), NheI (Nh), or EcoRV (V) shown on the map (F). Digesting genomic DNA from MCF7 with NcoI and NheI and hybridizing with a probe in the GAPF-positive region in 8q24.21 yielded abnormally sized fragments of 5 and 7 kb, respectively (white arrowheads), which differed from the expected 12-kb fragments based on the normal genome sequence. Note that we also detected normal-sized fragments, indicating the presence of rearranged and normally arranged alleles. (E) Snapback Southern to confirm palindromic nature of GAPF-positive region in 8q24.21. Genomic DNA from MCF7 (M) and IMR90 (I) were first digested with either NcoI or NheI. The digested samples were evenly split and half of the sample was processed through GAPF to create snapback DNA, shown in the + lanes. Note that the rearranged fragments in MCF7 (white arrowheads) were converted to half-sized fragments (black arrowheads) following GAPF. (F) Inferred restriction enzyme map of normal and palindromic loci is shown with the location of the palindromic center marked by the gray arrow. Probe location is denoted on inferred map.