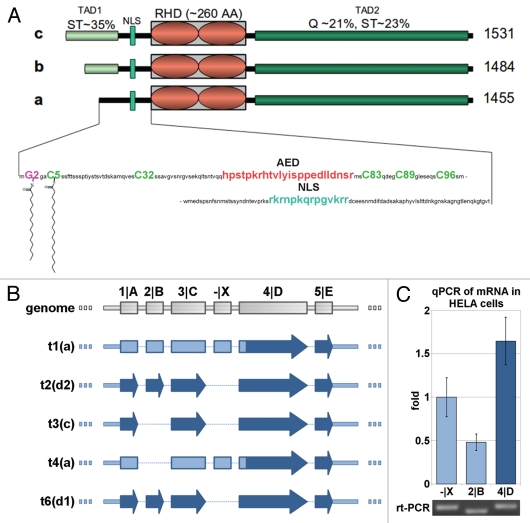
Figure 1.
Protein isoforms, transcripts and expression of NFAT5. (A) Schematic alignment of NFAT5 isoforms a, b and c. The 3 main protein domains are two transactivation domains (TAD1/2) and a Rel homology domain (RHD). Tad1 contains a hypothetical auxiliary export domain (AED) followed by a nuclear localization sequence (NLS). The three isoforms differ in their N-terminal sequence. Only NFAT5a has the N-terminal glycine for myristoylation (purple). Possible cysteines for palmitoylation (green) are indicated.Supplemental Material A contains a Table of NFAT5 orthologs and their alignment. (B) Schematic representation of the mRNA architecture for all known NFAT5 transcripts. The respective protein isoforms are indicated next to the transcript number by their letter codes. (C) Endogenous NFAT5a mRNA expression in HeLa cells was tested with qPCR. All three mRNA segments targeted, namely, -|X (occurring in transcripts 1 and 4, seeTable 1 andSup. Material A for the aligment of the transcripts), exon 2|B (occurring in transcripts 1, 2 and 6) and exon 4|D (occurring in transcripts 1–4 and 6), were found to be present in the cells. The PCR products were analyzed on an agarose gel, and the bands were sequenced to confirm the identity of the respective mRNA segments.