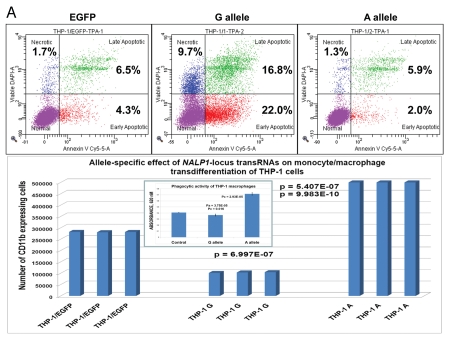
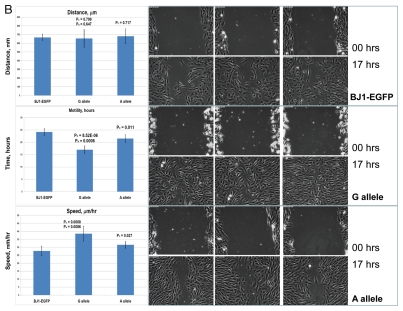
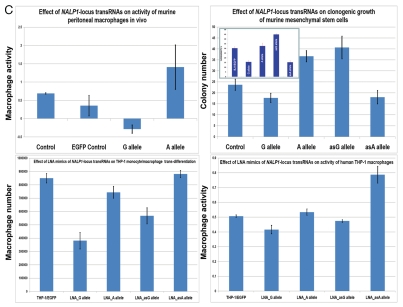
Figure 1.
Constitutive expression of distinct allelic variants of NLRP1-locus snpRNAs exerts allele-specific clinically relevant effects on phenotypes of human cells. (A) THP-1 cells were engineered to stably express distinct allelic variants of the NLRP1-locus snpRNAs and induced to differentiate into macrophages. Efficiency of the monocyte/macrophage transdifferentiation was assessed by analysis of viable and apoptotic cells (top parts) and measurements of the number (bottom parts) and phagocytic activity (inset, bottom part) of macrophages. Note that in response to induction of differentiation, THP-1 cells expressing pathology-linked G-allele snpRNAs undergo massive apoptosis and produce ∼5-fold less macrophages that are twice less potent in the sheep erythrocyte phagocytosis assay compared with macrophages derived from THP-1 cells expressing ancestral A-allele snpRNAs. Pathology-linked G allele-expressing human fibroblast BJ1 cells manifest significantly higher motility compared with ancestral A allele-expressing BJ1 cells. Gaps of defined distances were created in confluent cultures of BJ1 cells, and motility sequences were continuously monitored and recorded using time-lapse video cinematography. For each culture, the initial distance, motility sequence time (time to complete closing of the gap) and motility speed were measured. Average values of six replicate measurements are reported. Human NLRP1-locus snpRNAs manifest allele-specific biological activities in mouse macrophages (top left set of bar graphs) and mouse mesenchymal cells (top right set of bar graphs; inset shows results of the similar assay in human mesenchymal cells), which recapitulate the corresponding allele-specific biological activities in human cells. Bottom set of bar graphs shows the biological activities of synthetic 19 nt LNA-oligonucleotide-based structural analogs of the allele-specific variants of NLRP1-locus snpRNAs, which were assessed using THP-1 monocyte/macrophages transdiferentiation assays. Note that synthetic LNA analogs recapitulate the allele-specific patterns of NLRP1-locus snpRNA bioactivities mimicking effects on macrophage numbers (left) and phagocytic activity (right).