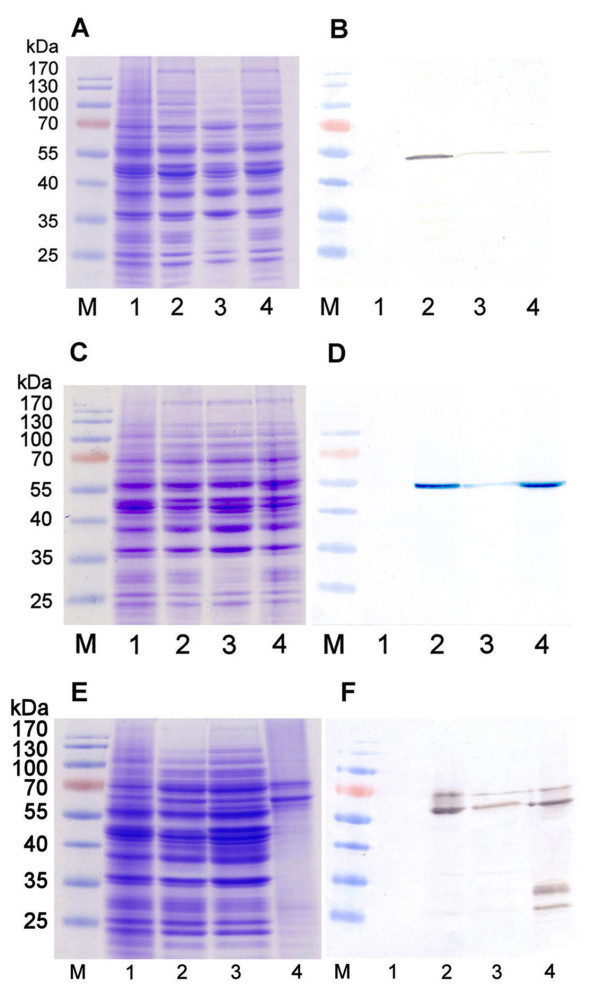
Figure 2.
Analysis of the production of anti-VLY scFv-Fv, His-scFv-Fv and αF-scFv-Fv proteins in yeast strain AH22-214p. (A, C, E): Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE; (B, D, F): Western blot with HRP-labeled secondary antibody against human IgG. (A, B): In lanes: 2-whole crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-scFv-Fc plasmid, 3-the soluble fraction recovered after centrifugation of whole crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-scFv-Fc plasmid, 4-pellet recovered after centrifugation of whole crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-scFv-Fc plasmid. (C, D): In lanes: 2-whole crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-His-scFv-Fc plasmid, 3-the soluble fraction recovered after centrifugation of crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-His-scFv-Fc plasmid, 4-pellet recovered after centrifugation of crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-His-scFv-Fc plasmid. (E, F): In lanes: 2-whole crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-αF-scFv-Fc plasmid, 3-the soluble fraction recovered after centrifugation of crude lysate of yeast transformed with pFX7-αF-scFv-Fc plasmid, 4-αF-scFv-Fc purified using protein A Sepharose (lane 4). In all gels negative control sample of whole crude lysate of S. cerevisiae cells, transformed with empty vector pFX7 was loaded on lane 1 and pre-stained protein weight marker (Thermo Scientific Fermentas) was loaded on lane M.