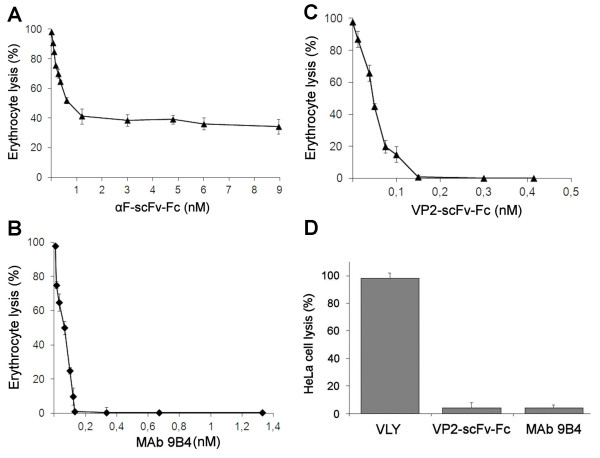
Figure 4.
Inhibition of VLY-mediated cytolysis by anti-VLY αF-scFv-Fc, mAb 9B4 and pseudotype VP1/VP2-scFv-Fc VLPs. (A, B, C): The inhibition of VLY-mediated lysis of human erythrocytes (% of hemolysis cells) was evaluated after addition of human erythrocyte suspension to VLY (5 ng/ml) pre-incubated with (A): αF-scFv-Fc protein at concentrations ranging from 3.6 ng/ml (6 × 10-11 M) to 540 ng/ml (8.96 x10-9 M); (B): MAb 9B4 at concentrations ranging from 1 ng/ml (6.7 × 10-11 M) to 200 ng/ml (1.33 × 10-9 M); (C): VP1/VP2-scFv-Fc VLPs at concentrations of VP2-scFv-Fc protein ranging from 1 ng/ml (1.25 × 10-11 M) to 33 ng/ml (4.1 × 10-10 M). (D): The inhibition of VLY-mediated lysis of human cervical epithelial HeLa cells was evaluated after their exposure to VLY alone (3 μg/ml) or VLY (3 μg/ml) preincubated either with VP1/VP2-scFv-Fc VLPs (VP2-scFv-Fc concentration 3 μg/ml or 3.8 × 10-8 M) or MAb 9B4 (50 μg/ml or 3.33 x10-7 M). Cell viability was determined by colorimetric assay using MTS staining. Values were normalized to 100% for each assay.