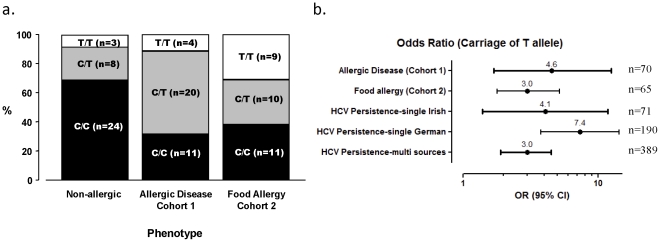
Figure 1. Variation at tagging SNP rs12979860 confers risk for allergic disease.
a. Carriage of the T allele of rs12979860 is over-represented in children with allergic disease (cohort 1, n = 70) (p = 0.004). This relationship is also observed for children with IgE-mediated food allergy (Cohort 2, n = 60) (p = 0.04 dominant model). For both cohorts, the frequency of the different genotypes varies between disease and control subjects (p = 0.02; cohort 1 and cohort 2). b. Odds ratio (OR; 95% CI) for carriage of T allele of rs12979860 and allergic disease and for HCV persistence. Odds ratio values for HCV cohorts are from di Iulio et al [20] and Tillman et al [28]. ORs for allergic disease and food allergy adjusted for gender. ORs for HCV cohorts adjusted for HBV co-infection in all cohorts and gender in the multiple source cohort.