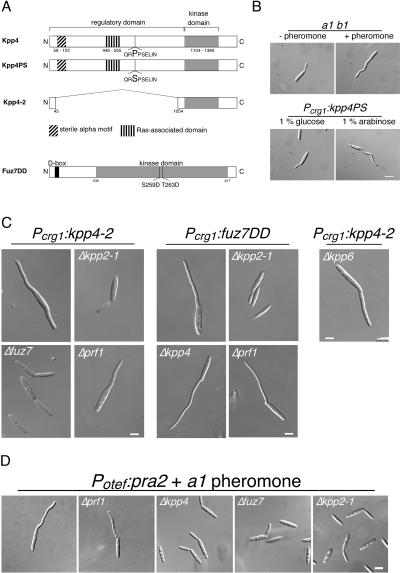
FIG. 2.
Constitutively active alleles of kpp4 and fuz7 induce conjugation tube-like structures. (A) Schematic representation of the kpp4 and fuz7 alleles used in this study. Kpp4PS harbors a P681S substitution in a conserved region, the so-called catalytic binding domain of STE11p-like kinases. In Kpp4-2 the regulatory domain is deleted. In Fuz7DD (accession number Q99078, 435 amino acids) two amino acid substitutions, S259D and T263D, were introduced in the conserved phosphorylation motif of MAPKK as described for, e.g., MEK1 (26). The D box (amino acids 13 to 21), described to be essential for MAPKK-MAPK interaction, is located in the N terminus of Fuz7 (6). (B) Expression of constitutively active kpp4PS induces structures that resemble conjugation tubes. FB1 cells were treated with a2 pheromone (upper right panel), and FB1Pcrg1:kpp4PS was incubated with arabinose for 4 h (lower right panel). All pictures were taken with the same magnification. Bar, 10 μm. (C) Kpp4, Fuz7, and Kpp2 act in one cascade. FB1 derivatives harboring either kpp4-2 or fuz7DD are indicated on top and with the indicated gene deletions were used. Cell morphology was scored at 5 h after growth in arabinose-containing medium. All pictures were taken with the same magnification. Bar, 5 μm. (D) Overexpression of the pheromone receptor rescues conjugation tube formation in prf1 deletion strains. FB2 and all FB2-derived strains expressed pra2 constitutively, carried the indicated gene deletions, and were stimulated with a1 pheromone. All pictures were taken with the same magnification. Bar, 5 μm.