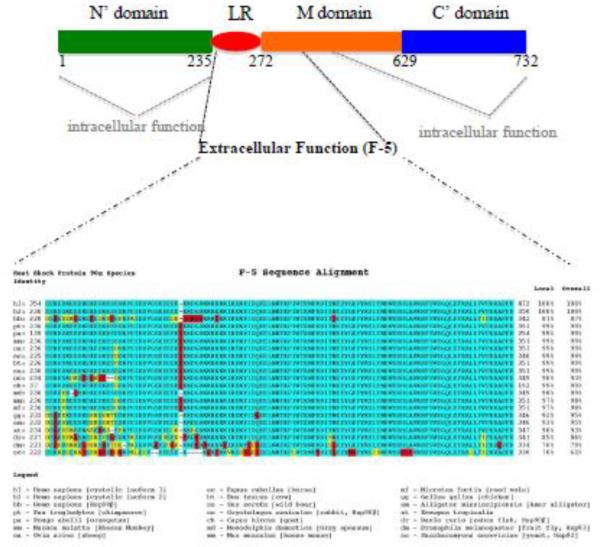
Figure 2. A schematic distinction of the functional elements for intracellular vs. extracellular Hsp90α.
(A) The intracellular chaperone function of Hsp90 requires almost the entire molecule, especially the amino terminal (green) and the carboxyl terminal (blue) domains. The extracellular pro-motility function of Hsp90α depends on less than a 115 amino acid fragment (F-5) located at the boundary between the LR and the M domains. This epitope appears at the surface of Hsp90 protein [ref. 13].
(B) F-5 is highly conserved during evolution of Hsp90 genes. Green, identify; Yellow: similarity; Red, distinction.