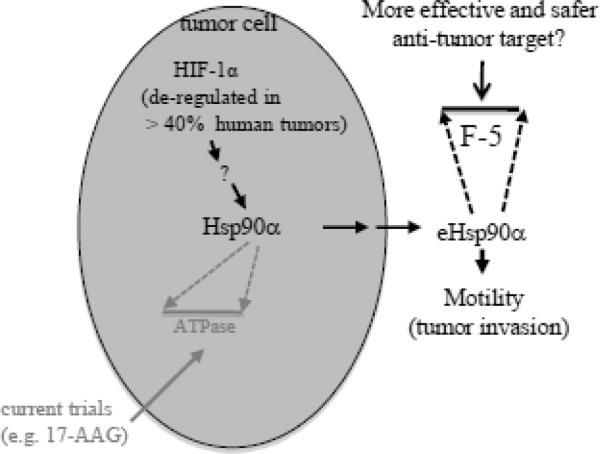
Figure 5. A model of secreted Hsp90α as a potential target for HIF-1α-positive cancers.
The severe hypoxia often found at the center of a stroma-surrounded tumor. Gene mutations in the tumor cells have caused constitutive accumulation of HIF-1α, even under normoxia. The deregulated HIF-1α triggers secretion of Hsp90α via exosomal protein trafficking pathway. The secreted Hsp90α binds, via F-5 epitope, to cell surface LRP-1 receptor and promotes motility and invasion of tumor cells in an autocrine fashion. While current clinical trials focus on intracellular Hsp90α, we propose that drugs that target the F-5 region of secreted Hsp90α are more effective and safer in treatment of cancer patients (Modified with permission from ref.32).