Fig. 6.
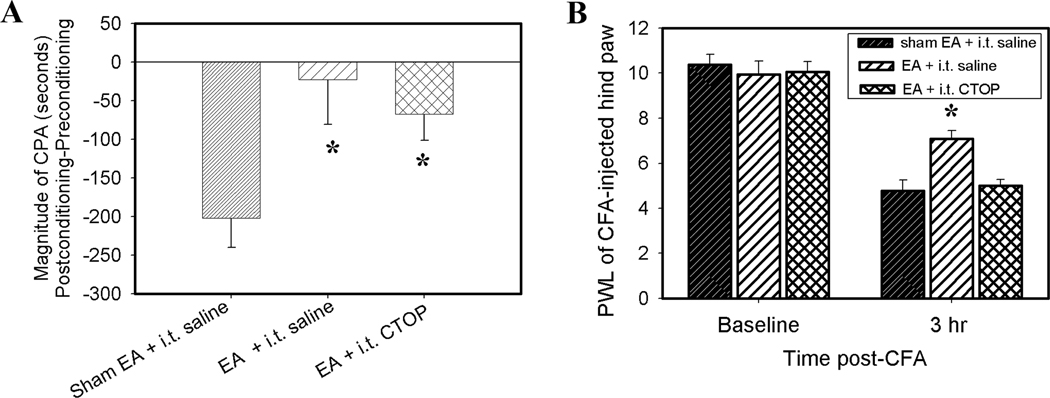
Fig. 6A. Effects of CTOP (5 nmol, i.t.), a mu-selective opioid receptor antagonist, on EA inhibition of CFA-induced affective response (n=6/group). EA plus saline (i.t.) or CTOP significantly inhibited CFA-induced affective response compared to sham EA plus saline (i.t.). This indicates that spinal CTOP did not block EA inhibition of the affective response. *P<0.05 vs sham EA + saline control. Fig. 6B. Effects of CTOP on EA inhibition of the nocifensive reflex (n=6/group). EA plus saline (i.t.) significantly increased PWL of the CFA-injected hind paw compared to sham EA plus saline (i.t.), suggesting EA inhibition of the nocifensive reflex. However, EA plus CTOP (i.t.) did not increase PWL of the CFA-injected hind paw compared to sham EA plus saline (i.t.), suggesting that spinal CTOP blocked EA inhibition of the nocifensive reflex.