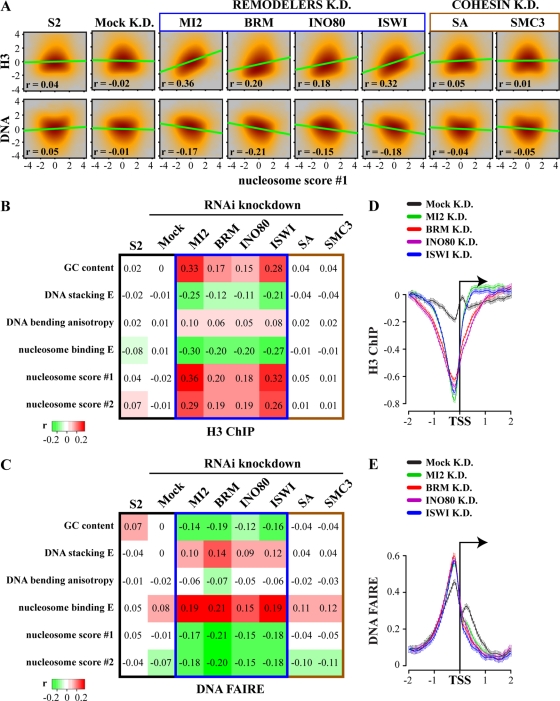
Fig 5.
Remodelers counteract genome-wide DNA sequence-driven nucleosome organization. (A) Remodeler depletion strongly increases the correlation between DNA sequence-derived nucleosome occupancy predictions and experimentally determined endogenous nucleosome organization. Smooth scatterplots of genome-wide histone H3 density or DNA accessibility versus nucleosome score 1 for cells depleted of the indicated remodeler ATPase are shown. The cohesin subunits stromalin (SA) and SMC3, as well as GFP (mock), were depleted as controls. Correlations (r) and linear regression lines are shown. (B and C) Heatmaps of the correlations between experimentally determined chromatin structure and DNA sequence-derived predictions genome-wide. Correlation between a variety of DNA sequence parameters and genome-wide H3 ChIP-chip occupancy (B) and FAIRE-chip-derived DNA accessibility profiles (C), before (S2 cells) or after depletion of the indicated remodeler ATPases, is shown. SA, SMC3, and GFP (mock) were depleted as controls. (D and E) Remodeler depletion affect chromatin conformation at promoters. Plots of averaged H3 occupancy (D) and DNA accessibility (E) at promoters of S2 cells, which were either mock treated (mock K.D.) or depleted of the indicated remodeler ATPases, are shown. Distance to the TSS is indicated, and whiskers for 95% CI are shown.