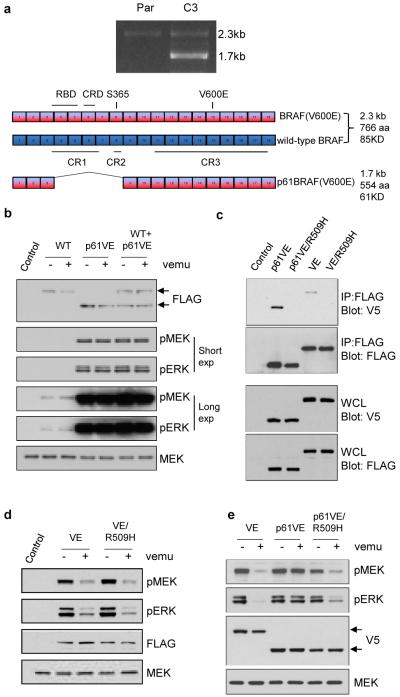
Figure 2. A BRAF(V600E) variant that lacks exons 4-8 is resistant to the RAF inhibitor vemurafenib.
a. PCR analysis of BRAF in cDNA from parental (P) and C3 cells. Sequencing of the 1.7kb product expressed in the C3 clones but not in parental cells revealed an in frame deletion of five exons (4-8) in cis with the V600E mutation. Abbreviations: CR1: Conserved Region 1, CR2: Conserved Region 2, CR3: Conserved Region 3, RBD: RAS-binding domain, CRD: Cystine-Rich Domain. b. Full length wild-type BRAF and the 1.7kb/61kd splice variant of BRAF(V600E) were expressed in 293H cells. The effect of vemurafenib (2μM for 1 hour) on ERK signaling in the presence of p61BRAF(V600E) was analyzed by western blot for pMEK and pERK. c. To compare levels of dimerization, 293H cells co-expressing FLAG tagged and V5-tagged p61BRAF(V600E), full length BRAF(V600E) and the corresponding dimerization-deficient mutants p61BRAF(V600E/R509H) and BRAF(V600E/R509H) were lysed followed by immunoprecipitation with FLAG antibody. Western blotting with V5 or FLAG antibodies was performed as indicated. d. Comparison of MEK/ERK activation and sensitivity of ERK signaling to vemurafenib (2μM for 1 hour) in 293H cells expressing either Flag-tagged BRAF(V600E) or the dimerization mutant Flag-tagged BRAF(V600E/R509H). e. Constructs expressing V5-tagged BRAF(V600E), p61BRAF(V600E) or the dimerization mutant p61BRAF(V600E/R509H) were transfected into 293H cells and treated with DMSO or 2μM vemurafenib for 1 hour.