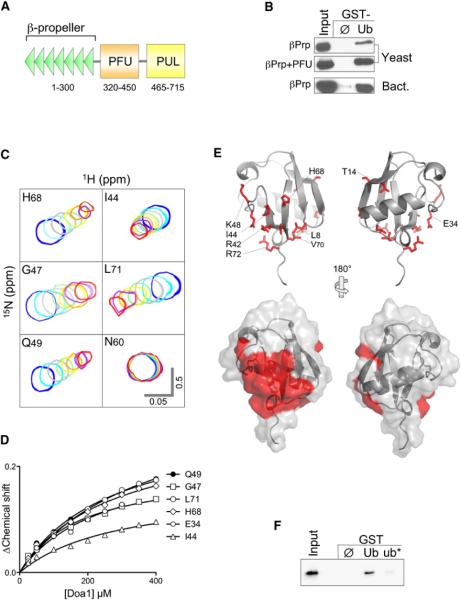
Figure 1. The Doa1 WD40 β-Propeller Binds Ub.
(A) Schematic of S. cerevisiae Doa1 domains including WD40 repeats forming the β-propeller, a central (P)LAA (F)amily (U)b-binding (PFU) domain, and a C-terminal (P)LAA, (U)fd3p and (L)ub1p (PUL) domain that binds to p97/Cdc48.
(B) V5-epitope-tagged fragments of Doa1 encompassing the N-terminal β-Prp, either alone or with the PFU domain, were expressed in yeast or bacteria and subjected to pull-down assays using GST alone (ø) or GST-ubiquitin (Ub). Samples were immunoblotted with anti-V5 antibodies. Input lysate sample represents a 10% equivalent.
(C) NMR HSQC data of 15N-Ub (25 μM) in the presence of Doa1 β-Prp. Peaks of the indicated backbone amides are shown in the absence (blue) or presence of increasing amounts of Doa1 β-Prp (Doa1:Ub molar ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 4:1, 6:1, 8:1,10:1, and 12:1). Scale bars indicate 0.5 ppm for the 15N dimension and 0.05 ppm for 1H dimension.
(D) Chemical shift perturbations in the titration series were quantified using the formula (0.2*[ΔN]2 + [ΔH]2)1/2 and plotted as a function of Doa1 β-Prp concentration yielding a Kd of 224 μM (±27 SD).
(E) Residues undergoing selective chemical perturbation (+1 SD above the mean ΔChemical Shift) data from HSQC data of 15N-Ub and Doa1 at a 1:1 ratio were mapped onto the structure of Ub (PDB ID code 1UBQ). Side chains corresponding to the residues with the highest perturbations are red. Below is the corresponding molecular surface of Ub indicating a large contiguous patch of residues including L8, R42, I44, V70, and R72 that may form the Doa1 β-Prp-binding interface.
(F) Bacterially produced V5-Doa1 β-Prp was subjected to GST pull-down assays with GST alone (ø); or GST fused to wild-type ubiquitin (Ub); or ubiquitin with L8A, R42E, and I44A mutations (ub*). Input lysate represents a 10% equivalent.