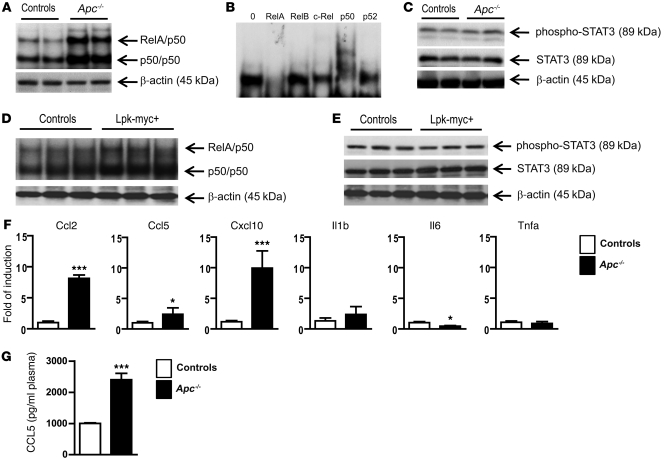
Figure 5. β-catenin activation in hepatocytes triggers an intrinsic inflammatory program associated with the activation of NF-κB.
(A–E) NF-κB activation (A) in liver nuclear extracts from Apc–/– and control livers was monitored by EMSA analysis. Supershift analysis (B) was performed to determine which NF-κB subunit was involved in Apc–/– livers. Immunoblotting was used to detect phospho-STAT3, STAT3, and β-actin (C) in protein lysates from Apc–/– and control livers. NF-κB activation (D) in liver nuclear extracts from Lpk-myc+ and control livers was monitored by EMSA analysis. (E) Immunoblotting was used to detect phospho-STAT3, STAT3, and β-actin in protein lysates from Lpk-myc+ and control livers. (F) mRNAs were extracted from NPCs and analyzed by real-time qPCR using specific primers. (G) Sera from Apc–/– and control mice were collected and CCL5 plasma levels were evaluated using Luminex technology (Bio-Rad). All data with statistical analysis are representative of 4 experiments with 4 mice/group. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 (controls versus Apc–/–). Error bars represent SD.