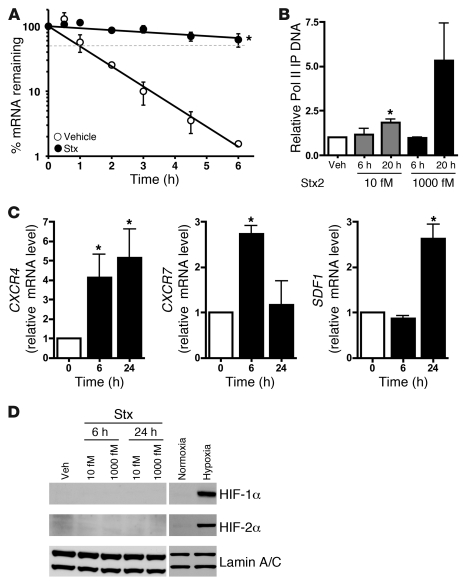
Figure 3. Stx enhances CXCR4 expression by both transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms.
(A) HMVECs treated with vehicle or 1,000 fM Stx2 for 20 hours were subjected to transcription arrest with 10 μg/ml actinomycin D, and RNA was harvested at various times thereafter. Remaining CXCR4 mRNA was determined using qRT-PCR and normalized to 18S. The mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is shown. Half-lives were calculated using exponential regression to be 1.18 ± 0.09 hours in vehicle-treated cells and 19.2 ± 7.8 hours in Stx-treated cells. (B) HMVECs were exposed to 1,000 fM Stx2 for 20 hours, followed by ChIP using anti-RNA polymerase II (Pol II) antibodies. qRT-PCR for CXCR4 was then used to determine the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA (IP DNA). The mean ± SEM of at least 4 independent experiments is shown. (C) HMVECs were maintained under normoxic (21% O2) or hypoxic (<1% O2) conditions for the indicated times. qRT-PCR was used to determine mRNA levels. Data are normalized for 18S levels and are shown relative to normoxic cells. The mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is shown. Similar trends were observed whether or not data are normalized to housekeeping genes. (D) Western blot analyses were performed for HIF-1α and HIF-2α in HMVECs treated with 10 fM or 1,000 fM Stx for 6 or 24 hours. Lamin A/C was used as a loading control. Negative control and positive control were normoxic and hypoxic HMVECs. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle or normoxia.