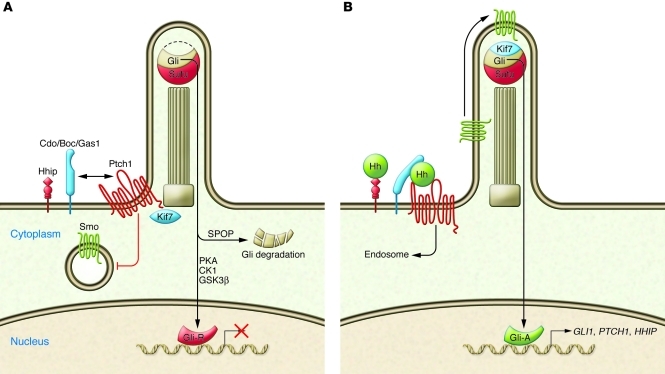
Figure 2. The Hh signaling pathway — a simplified model.
(A) In its “off” state, Ptch1 represses Smo activity. Gli2 and Gli3, effectors of the Hh pathway, are phosphorylated by a kinase cascade, which includes PKA, CK1, and GSK3β, and are directed to the proteasomal degradation pathway via the SPOP complex. A fraction of the Gli2/3 protein is processed into a repressor form, Gli-R, which inhibits Hh target gene transcription. (B) Hh ligand binding to Ptch1 abrogates its inhibitory effect on Smo, allowing Smo to translocate into the primary cilium and induce accumulation of the Gli-Sufu complex at the tip of the primary cilium. Activation of the Hh pathway results in accumulation of Gli-A and initiation of the transcription of Hh target genes such as PTCH1, GLI1, and HHIP.