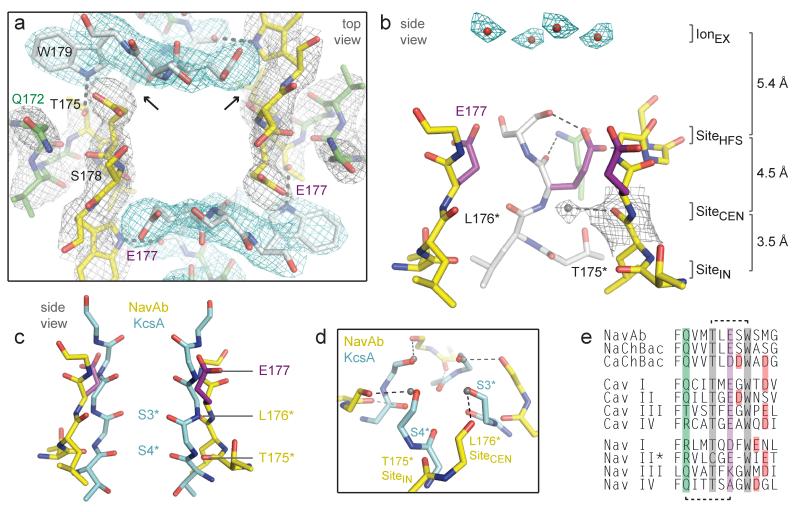
Figure 3. Structure of the NavAb selectivity filter.
a, Top view of the selectivity filter. Symmetry-related molecules are colored white and yellow; P-helix residues are colored green. Hydrogen bonds between Thr175 and Trp179 are indicated by grey dashes. Electron-densities from Fo-Fc omit maps are contoured at 4.0 σ (blue and grey) and subtle differences can be appreciated (small arrows). b, Side view of the selectivity filter. Glu177 (purple) interactions with Gln172, Ser178 and the backbone of Ser180 are shown in the far subunit. Fo-Fc omit map, 4.75 σ (blue); putative cations or water molecules (red spheres, IonEX). Electron-density around Leu176 (grey; Fo-Fc omit map at 1.75 σ) and a putative water molecule is shown (grey sphere). Na+-coordination sites: SiteHFS, SiteCEN and SiteIN. c, Superposition of NavAb and a K+-channel selectivity filter: NavAb Glu177 side-chains (purple) and backbone carbonyls (*); K+-channel (blue, 1K4C), site 3 and site 4 backbone carbonyls (ref. 35) (*). This structural alignment is based on P-helices. d, Enlarged view of SiteCEN and SiteIN: water molecules, grey spheres; dotted lines, ~2.5 Å. e, Selectivity filter sequence alignment. E177 homologs, purple; outer-ring of negatively charged residues (red).