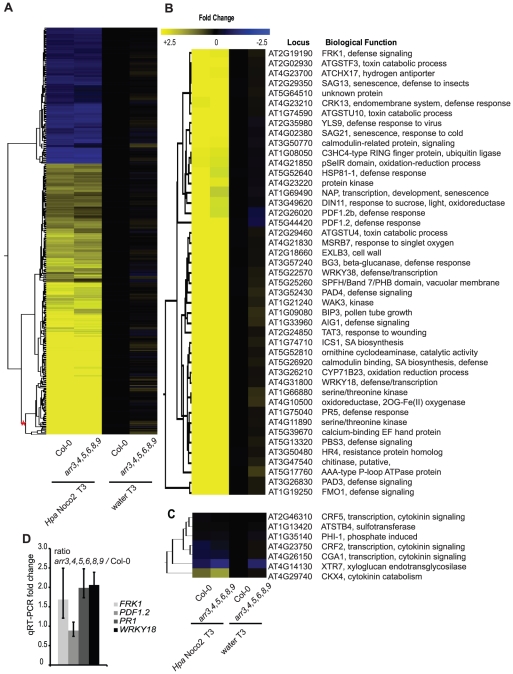
Figure 5. Type-A ARRs negatively regulate SA–dependent gene expression.
(A) Transcriptome analysis of type-A arr3,4,5,6,8,9 mutant plants in response to Hpa Noco2. Two-week-old wild-type or type-A arr3,4,5,6,8,9 mutant plants were inoculated with either water or Hpa Noco2. Tissue was harvested at 3 dpi. For the analysis, wild-type water-treated samples were used as a baseline. Genes up- or down-regulated at least two-fold by Hpa Noco2 in wild-type plants were selected. Hierarchical clustering (K-means) of Hpa Noco2-regulated genes in wild-type plants is shown. See also Table S1. (B) Subset of Hpa Noco2-regulated genes with altered expression in the arr3,4,5,6,8,9 mutants. Hpa Noco2-regulated genes from the most highly regulated cluster from (A) (red asterisk) that are differentially regulated in unchallenged arr3,4,5,6,8,9 mutant plants. (C) Representative cytokinin-regulated genes that are also Hpa Noco2-regulated. (D) qRT-PCR of select genes from (A). Two-week-old wild-type or arr3,4,5,6,8,9 plants were inoculated with water. RNA was extracted from tissue harvested three days later. Levels of the indicated transcripts were determined by qRT-PCR relative to wild-type plants. Error bars represent SE from three technical replicates and correspond to upper and lower limits of 95% confidence intervals. Data from one biological replicate are shown.