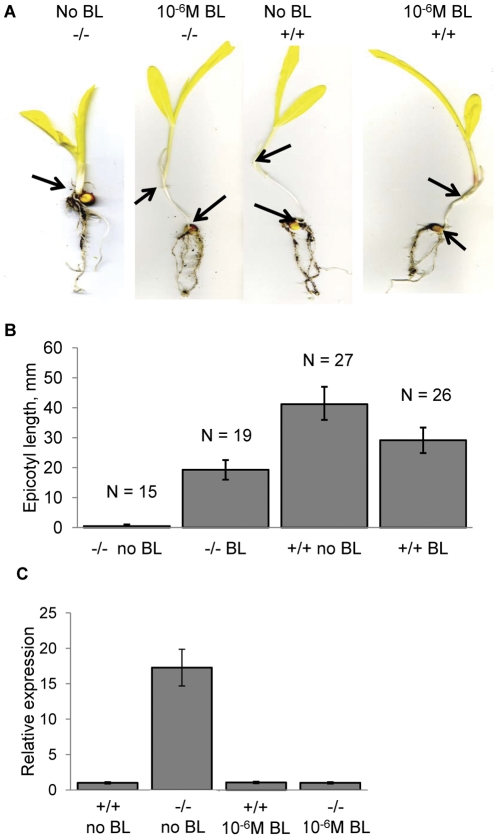
Figure 3. Supplementing the growth media with 10−6 M brassinolide (BL) partially rescues the brd1 –m1 phenotype in maize.
Plants were germinated and grown in the darkness on MS medium with or without 10−6 M brassinolide. At 12 days after planting the seedlings were genotyped and wild type (+/+) and mutant (−/−) plants were identified. A brd1-m1 plants grown on media supplemented with brassinolide show epicotyl elongation, while mutant plants grown without brassinolide fail to show etiolation response. Arrows indicate the positions of the internodes. B Epicotyl length was measured in 12 day old seedlings germinated and grown in the darkness. The results are presented as mean values +/− standard deviation from four to eight plants. All of the groups exhibit statistically significant differences at p<0.01 or less (t-test). Number of plants in each category is shown above each of the columns. C qRT-PCR analysis of the brd1 expression level. The expression level of brd1 was normalized to the expression of the house-keeping mez2 gene and shown relative to the expression of the wild type plants grown without brassinolide. No RT controls were all negative (data not shown). The difference between the brd1 expression in mutant plants grown without brassinolide supplement and all other growth conditions is statistically significant at p<0.001 (t-test). The data are presented as mean values +/− standard deviation from three samples for each growth condition.