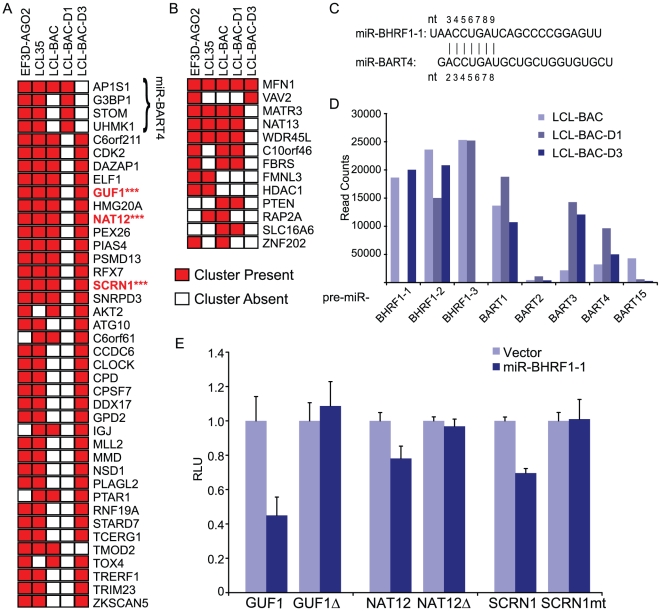
Figure 4. High confidence targets of EBV miR-BHRF1-1 and miR-BHRF1-3.
A. 3′UTR clusters assigned to miR-BHRF1-1 (minimum seed match: 7mer1A) that were present in at least three of the five PAR-CLIP libraries and are specific to EBV-infected LCLs are shown in red with annotated gene symbols. Clusters that were absent from the LCL-BAC-D1 PAR-CLIP library are shown in white, and therefore, represent high confidence targets for miR-BHRF1-1. The four miR-BHRF1-1-assigned clusters present in LCL-BAC-D1 can also be assigned to miR-BART4-5p. B. Similar to A, 3′UTR clusters assigned to miR-BHRF1-3 that were present in at least two PAR-CLIP libraries are shown in red; clusters absent from the LCL-BAC-D3 library are shown in white. C. Alignment of miR-BHRF1-1 and miR-BART4-5p, which share an off-set seed sequence. D. EBV pre-miRNAs detected in LCL-BAC, LCL-BAC-D1, and LCL-BAC-D3 as determined by deep sequencing. Reported are the total number of reads mapping to each EBV pre-miRNA. E. PAR-CLIP identified seed match sites to miR-BHRF1-1 in three 3′UTRs (***highlighted in A) were deleted (GUF1 and NAT12) or mutated to an NheI restriction enzyme site (SCRN1) in luciferase reporter vectors to disrupt miRNA binding. Luciferase assays were performed as in Figure 3 and values are shown relative to an internal renilla luciferase control.