Figure 4. Induction of Treg cells requires B7-H1.
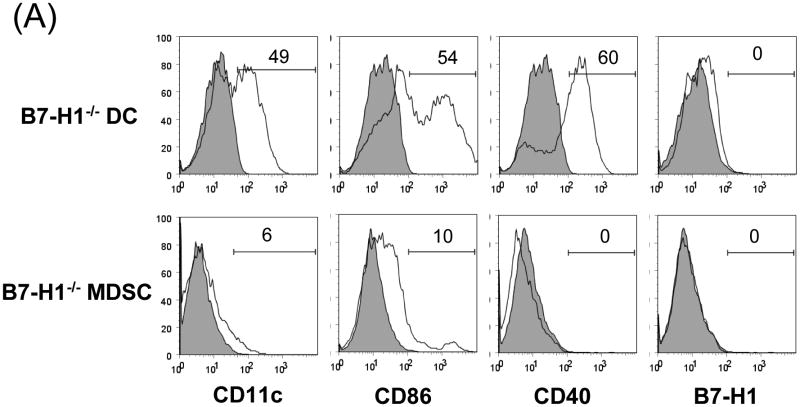
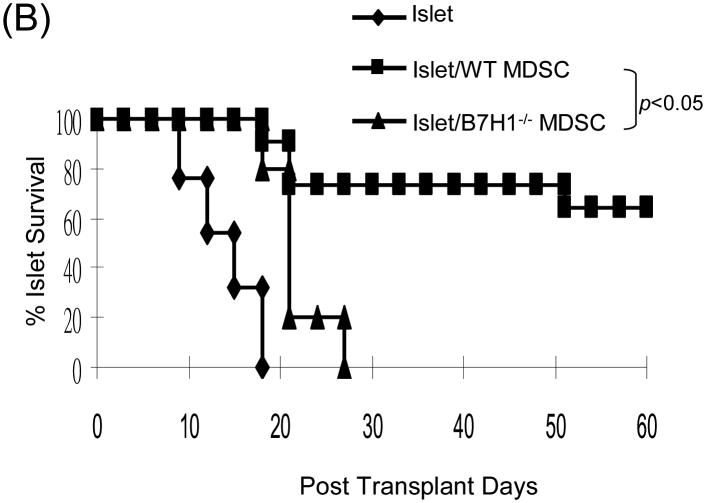
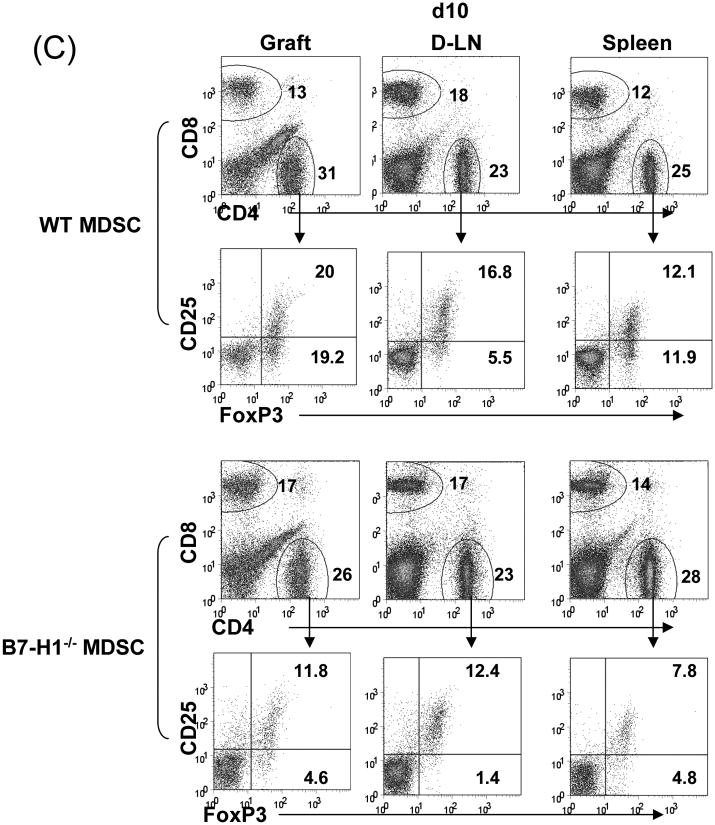
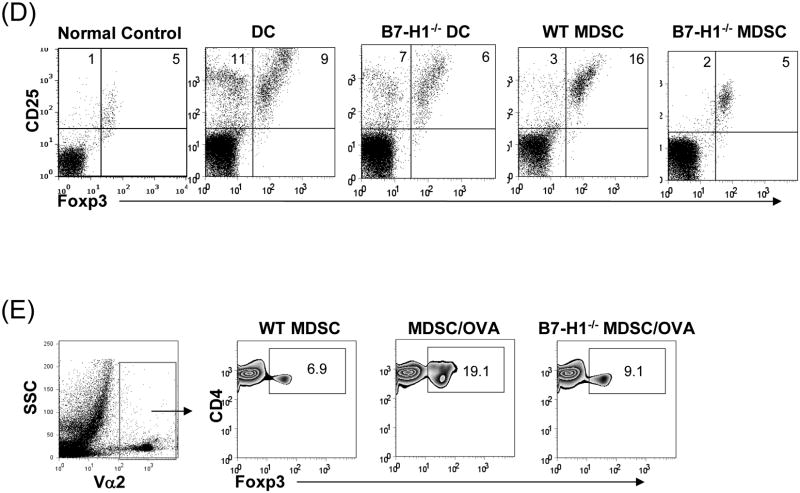
(A) Phenotype of MDSC generated from B7-H1-/- mice. B7-H1-/- DC and MDSC were stained for CD11b, CD11c and the key surface molecules, analyzed by flow cytometry gated on CD11b+ cells, and expressed as hitograms (filled area is isotype control). (B) B7-H1-/- MDSC lose ability to protect islet allografts and expand Treg cells. 2 × 106 B7-H1-/- or wild type (WT) MDSC mixed with 300 BALB/c islets were transplanted into diabetic B6 recipients (islet grafting alone served as control). Left panel: islet graft survival. Right panel: Cells isolated from the islet grafts, D-LN and spleen on POD 10 were stained for CD4, CD8, CD25 and Foxp3. Expression of Foxp3 and CD25 were analyzed by flow cytometry gated on CD4+ cells. (C) Failure of B7-H1-/- MDSC to expand Treg cells in vitro. B6 DC or MDSC (either WT or B7-H1-/-) were cultured with BALB/c spleen T-cells [at a ratio of 1:20, and in the presence of IL-2 (10U/ml)] for 3 days. Treg cells were analyzed by flow cytometry gated on CD4+ cells. (D) Failure of B7-H1-/- MDSC to expand Treg cells in vivo. Normal B6 mice were adoptive transferred (i.v.) with 107 OVA specific CD4+ T cells (from OT II mice), while footpad was injected with 5 × 105 B7-H1-/- or wild type (WT) MDSC pulsed with OVA protein (100 μl/ml overnight). Footpad injection with WT MDSC without antigen pulse served as control. Lymphocytes were isolated from the popliteal lymph nodes (injected side) 3 days later, and analyzed by flow for expression of CD4, Foxp3 gated on Vα2+ (OT II phenotypic) cells. The data are representative of two separate experiments. The number is percentage of positive cells.