Figure 1.
Mapping the BUBR1-Blinkin Interaction
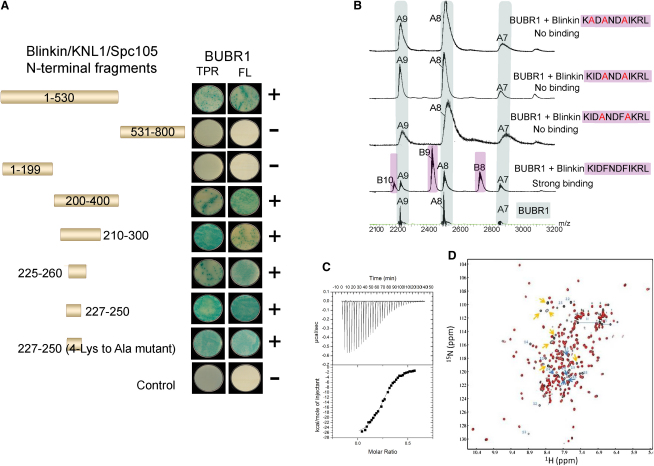
(A) BUBR1 interacts with N-terminal Blinkin fragments in a Y2H assay. Strains Y187[pGBKT7-bait] and GOLD[pGADT7-target] were mated and X-α-Gal activity assays performed on colonies grown on SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp plates. Colony growth requires the activation of ade and his reporter genes and the blue-producing X-α-Gal reaction requires the activation of the mel1 reporter gene to express the secreted reporter enzyme α-galactosidase.
(B) Nano-ESI MS of synthetic peptides that mimic Blinkin S208-K226 confirm the interaction while peptides harbouring site-specific substitutions indicate the hydrophobic residues I213, F215, F218 and I219 are critical for binding BUBR1.
(C) ITC data shows the affinity of the interaction (Kd = 9 μM); ΔH and ΔS of −2.7 kcal mol-1 and −64 kcal mol-1, respectively. Saturation of BUBR157-220 with Blinkin peptide S208-K226 was achieved when BUBR157-220 at concentration 27 μM was used to titrate against 200 μM of the peptide.
(D) An overlay of the 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra of BUBR1-Blinkin chimera (red) and free BUBR1 after addition of up to 2 moles of Blinkin peptide to one mol of protein. All structured amides from BUBR1 occupy an identical position in the chimera. Some extra peaks from the additional residues in the chimera are indicated: (blue, residue number shown) residues from Blinkin, which become structured upon binding and (orange) unstructured residues from the linker and extreme N terminus of Blinkin (see also Figure S1).