Fig. (4).
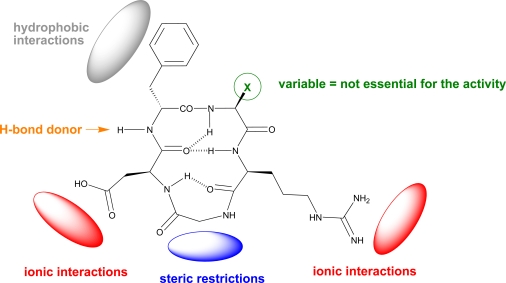
The tripeptide sequence Arg-Gly-Asp is essential for the activity and does not allow any other amino acid combination. Arg and Asp residues might promote ionic interactions with the receptor (with the carboxylate of Asp coordinating divalent cations) whereas the Gly imposes steric restrictions. Position 4 requires a hydrophobic residue in the D-configuration (i.e. D-Phe) for optimal side chain orientation and interaction with the receptor. The amide bond between residues 3 and 4 also participates in the binding and therefore may act as a hydrogen bond donor. Finally, position 5 can accommodate a number of residues without an impact in the biological activity.