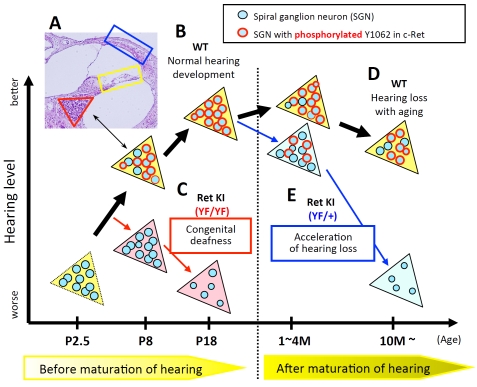
Figure 1.
Schematic summary of c-Ret-mediated SGNs loss. (A) Inner ear from a wild-type (WT) mouse at postnatal day (P) 14 stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Red triangle, yellow square and blue square contain spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs), inner- and outer-hair cells and the stria vascularis, respectively. Our morphological analyses showed almost no abnormalities in these areas besides SGNs from c-Ret-KIY1062F/Y1062F-mice. (B-E) Colored triangles in the schema represent Rosenthal's canals in WT (yellow triangles), homozygous c-Ret-KIY1062F/Y1062F(Ret KI (YF/YF), pink triangles) [1] and heterozygous c-Ret-KIY1062F/+-mice (Ret KI (YF/+), light blue triangles) [18]. Blue circles with a “black” line in the triangles represent SGNs. Blue circles with a “red” line in the triangles represent SGNs with “phosphorylated Y1062 in c-Ret". X-axis and Y-axis indicate age of mice and hearing levels, respectively. (B) WT mice showed that c-Ret protein was constantly expressed in SGNs (P1-18), while the numbers of Y1062-phosphorylated SGNs (blue circles with “red” line in yellow triangles in B) were sharply increased around P6-7, several days before the WT mice begin to acquire intact hearing levels (around P12∼) [1]. (C) c-Ret-KIY1062F/Y1062F-mice suffered from congenital deafness with decreased cell density of SGNs. c-Ret-KIY1062F/Y1062F-mice showed no Y1062-phosphorylated SGNs even on P8, although Y1062-phosphorylated SGNs began to appear in WT mice from P6 [1]. (D) WT mice (10 months old) showed hearing loss with aging. (E) c-Ret-KIY1062F/+-mice, in which the number of Y1062-phosphorylated SGNs was about half of that in WT mice (light blue triangles), suffered from acceleration of age-related hearing loss with decreased cell density of SGNs without functional and morphological abnormalities of hair cells [18]. Acceleration of age-related hearing loss in c-Ret-KIY1062F/+-mice was rescued by introducing constitutively activated RET [18].