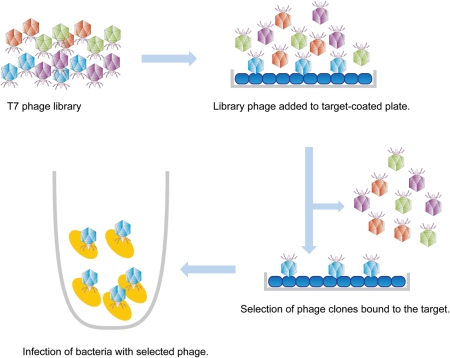
Fig. 1.
Biopanning of T7-based peptide-displaying phage library. A phage library consisting of as many as 109–10 clones is added to a plastic well coated with a target, such as a monoclonal anti-carbohydrate antibody. Phage clones that do not bind the target will be washed away from the plate. Competent host bacteria are then added to the well, so that phages remaining in the well will infect bacteria. Following the growth of infected bacteria, the phages are amplified. By repeating this procedure 3–4 rounds, phage clones displaying peptides with high target-binding affinity are isolated. Biopanning of the filamentous M13-based phage can be done in a similar manner.